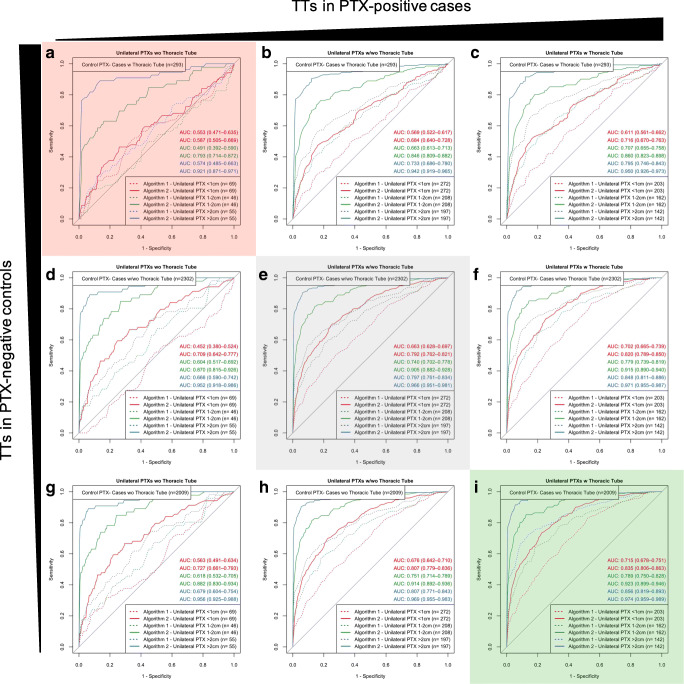
Fig. 3.
Detailed subgroup analysis (“Algorithm 1,” “Algorithm 2”) revealed thoracic tubes to be relevant confounders that can significantly bias algorithm performance. Subgroups based on PTX sizes are built for every subfigure; subfigures differ in whether PTX-positive cases and PTX-negative controls show inserted TTs. Overall performance is illustrated in the center (grayish highlighted). AUROCs for all subgroups negatively correlate with the proportion of inserted TTs in PTX-negative controls (decreasing from top to bottom). AUROCs for all subgroups positively correlate with increasing proportions of inserted TTs in PTX-positive cases (increasing from left to right). Resulting extreme scenarios are highlighted in red (algorithm discriminative performance strongly reduced) and green (best algorithm performance). Areas under receiver operating curves are illustrated including the 95% confidence intervals. PTX-positive cases that do not meet the subgroup PTX size definitions have been excluded from ROC analysis