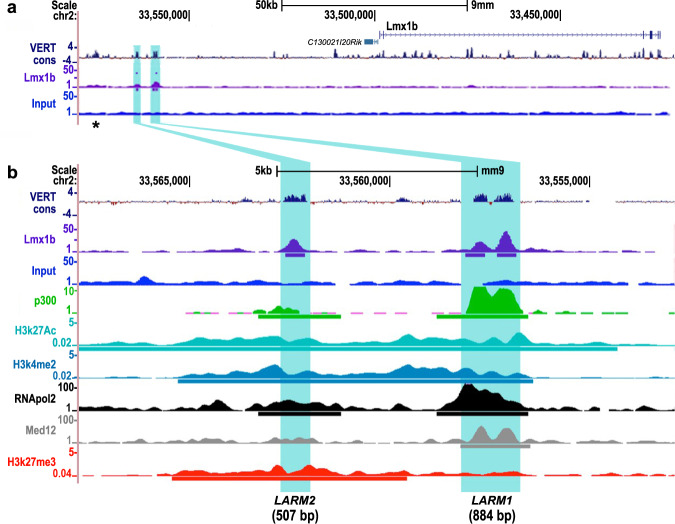
Fig. 1. LARM1 and LARM2 are conserved, bound by Lmx1b, and associated with active chromatin marks.
a UCSC genome screenshot displaying the Lmx1b locus and the associated cis-regulatory modules LARM1 and LARM2 (highlighted in blue) showing vertebrate conservation (VERT cons), Lmx1b binding (Lmx1b-targeted ChIP-seq)8 and input8. b Magnification of the putative enhancer region displaying the overlap with active enhancer-associated regulatory marks present in limb buds. From top to bottom: vertebrate conservation (VERT cons), ChIP-seq tracks for Lmx1b8, control Input limb DNA8, p30010, histone 3 acetylation at lysine 27 (H3K27Ac)11, histone 3 dimethylation at lysine 4 (H3K4me2)12, RNA polymerase II13, Med 1213, and histone 3 trimethylation at lysine 27 (H3K7me3)12. Note that LARM1 consists of two conserved peaks, both of which are recognized by Lmx1b-targeted ChIP-seq8. Upstream of LARM2, another conserved region is present (asterisk). This potential cis-regulatory module is also associated with the 9430024E24Rik gene21, but does not appear to be bound by Lmx1b, as shown in the Lmx1b-targeted ChIP-seq track (see also Supplementary Fig. 2).