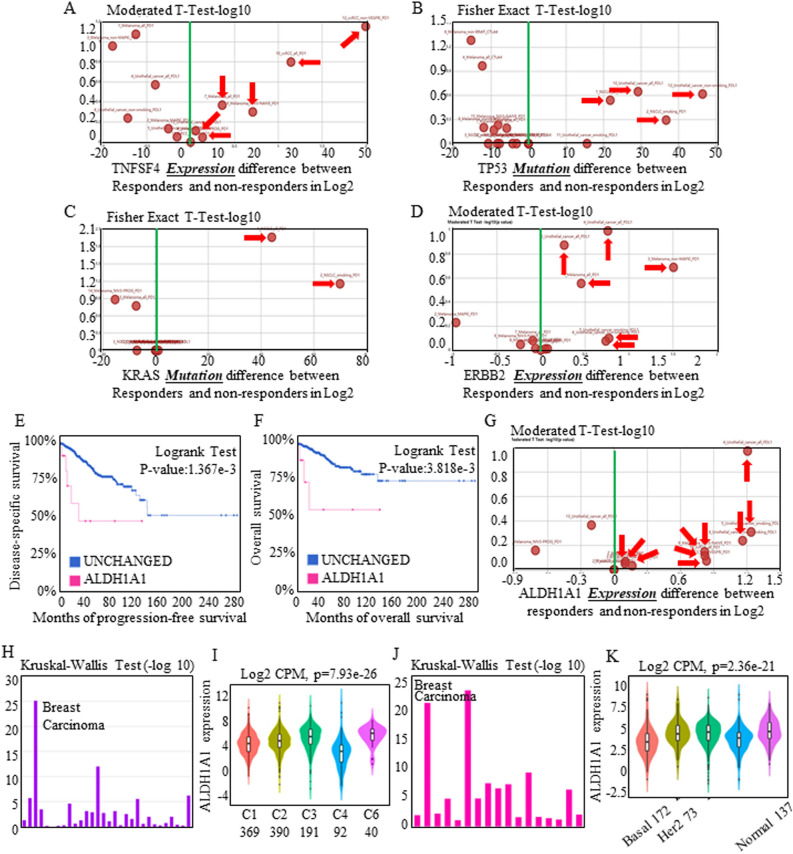
Figure 5.
TNFSF4 blockade therapies could be assessed in the stem cell signature-associated mode. The transcriptomic and genomic profiles of pretreated tumor biopsies from responders and non-responders treated with anti-PDL1 and anti-PD1 antibodies were enrolled for analysis. In total, the responders tended to exhibit higher TNFSF4 expression levels, and each study could be reviewed by searching for a certain PMID number (red labeling). Assessment of real-world immunotherapeutic effects indicated that effects related to TNFSF4 (A) tended to imply better outcomes and that TNFSF4-associated TP53 (B), KRAS (C), and ERBB2 (D) all indicated better immunotherapy response. Increased ALDH1A1 expression indicated shorter disease-specific survival (E) and overall survival (F), and ALDH1A1 surprisingly correlated with higher therapeutic response ratios (G) through clinical data assessment. (H,I) ALDH1A1 was analyzed for its roles in predicting immunotherapy response, and the 5 subgroups C1 (N = 369), C2 (N = 390), C3 (N = 191), C4 (N = 92), and C6 (N = 40) were involved in assessing functional aspects. ALDH1A1 expression dominated in all the subtypes, participating in multiple immune reaction processes. (J,K) Associations between ALDH1A1 expression and molecular subtypes across human cancers were also identified, and the signature of increasing ALDH1A1 expression tended to be found in all kinds of breast carcinomas. Specifically, C1 represents wound healing, C2 represents IFN-gamma dominant, C3 represents inflammatory, C4 represents lymphocyte depleted, C5 represents immunologically quiescent and is not shown, and C6 represents TGF-b dominant.