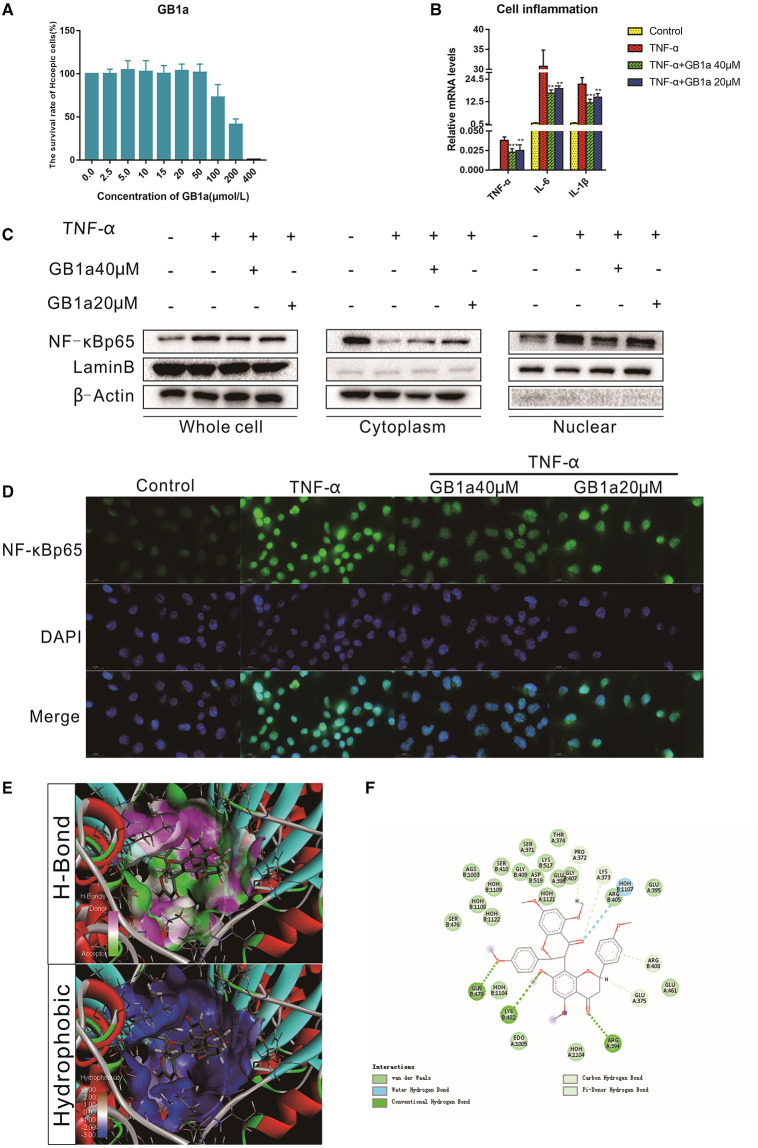
Figure 1.
The anti-inflammatory effects of GB1a are mediated by inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation in vitro (A) CCK8 analysis showed the cytotoxicity of GB1a on HCoEpic at different doses. (B) GB1a administration reduced the expression of intracellular pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β) in TNF-α-incubated HCoEpic in a dose-dependent manner. (C) GB1a treatment could inhibit NF-κB p65 protein expression in the nucleus and block NF-κB p65 translocation to the nucleus. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of NF-κB (green) in HCoEpic. DAPI was used for nuclear staining (blue). (E) The 2D structure of the predicted binding of GB1a to NF-κB. (F) The molecular docking model of GB1a and NF-κB. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 5/group). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.vs the TNF-α-incubated group.