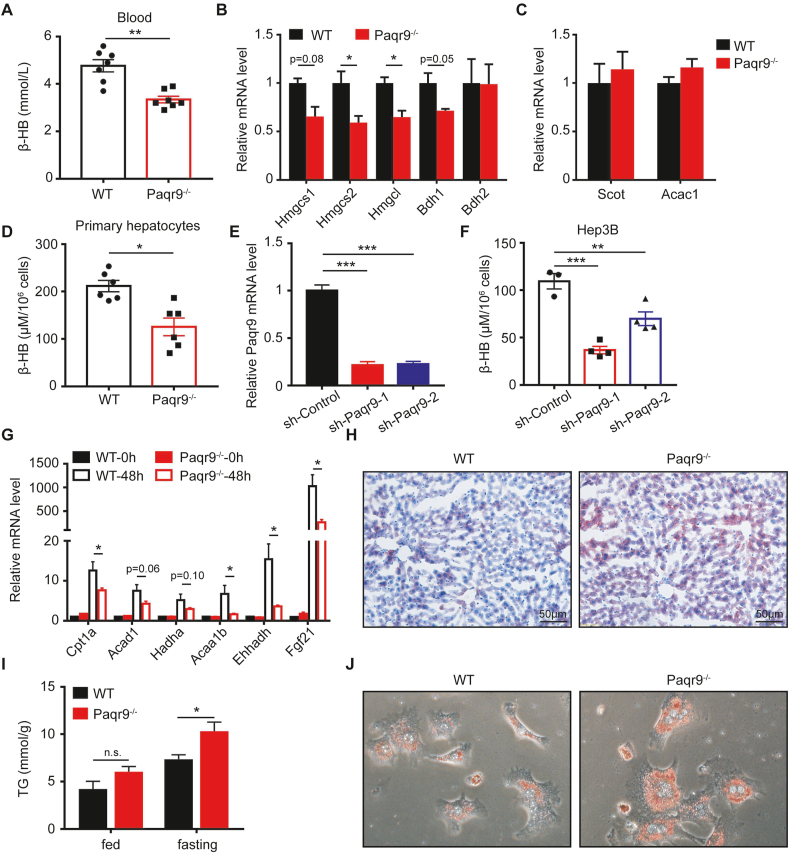
Figure 3.
Deletion of Paqr9 reduces hepatic ketogenesis and fatty acid oxidation in vivo and in vitro.A. Concentration of β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HB) in serum of the male wild type (WT) and Paqr9−/− mice after fasting for 24 hours (n = 6 for WT and n = 7 for Paqr9−/− mice). B. The mRNA levels of ketogenic genes in the liver of the mice, as in A. C. The mRNA levels of ketone degradation genes in the skeletal muscle of the mice, as in A. D. Concentration of β-HB in culture medium of primary hepatocytes isolated from the mice. The cells were treated with 500 μM sodium caprylate for 24 hours before measurement. E. Efficiency of Paqr9 knockdown in Hep3B cells transfected with shRNA-containing plasmids. F. Concentration of β-HB in culture medium of the cells, as in E. G. The mRNA levels of fatty acid β-oxidation genes in the livers of the mice after fasting for 48 hours. H. Representative images of Oil Red O staining of the livers from the mice after fasting for 24-hour fasting. I. Triglyceride level in the livers of the mice under feeding or fasting for 24 hours. J. Representative images of Oil Red O staining of primary hepatocytes isolated from the mice. The hepatocytes were treated with 1 g/L glucose and 500 μM sodium caprylate for 36 hours. All data were analyzed with Student's t-test. All the quantitative data are shown as mean ± S.E.M., ∗ for P < 0.05, ∗∗∗ for P < 0.001, and n. s. for non-significant.