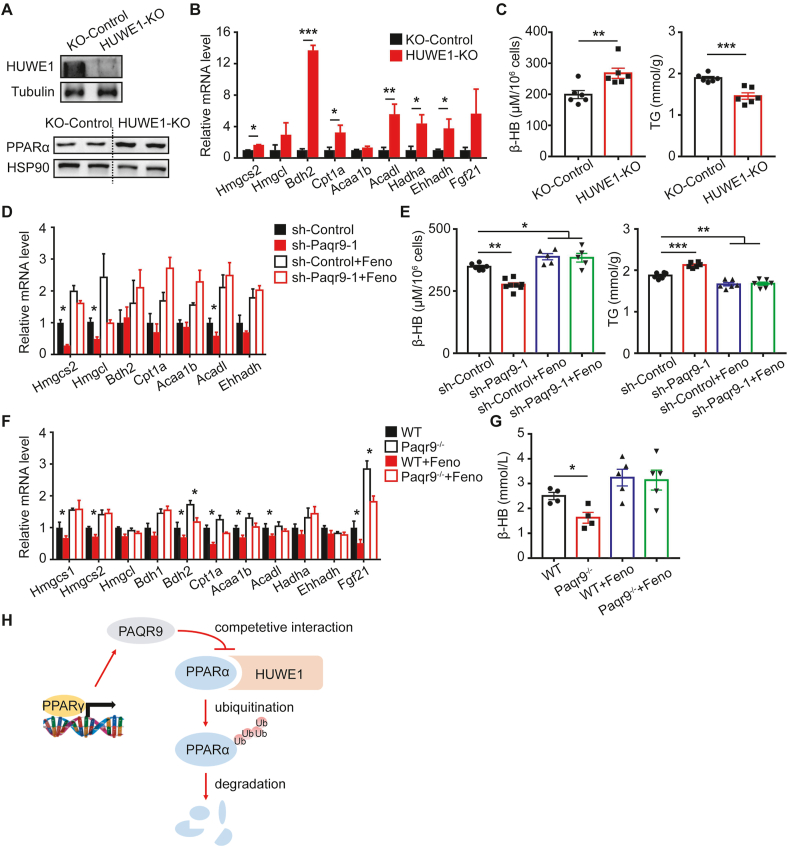
Figure 6.
PAQR9 affects ketogenesis and fatty acid oxidation through PPARα.A. HUWE1 deletion increases the protein level of PPARα in Hep3B cells. Upper panel: Western blotting to detect the efficiency of HUWE1 knockout. Lower panel: Western blotting to analyze PPARα protein level. B. Hep3B cells with or without HUWE1 knockout were treated with 1 g/L glucose and 500 μM sodium caprylate for 48 hours, followed by quantitative RT-PCR to analyze expression of genes involved in ketogenesis and FAO (n = 6 for each group). C. The cells, as in B, were used to measure β-HB level in culture medium and triglyceride concentration in the cells. D. HepB3 cells with or without Paqr9 knockdown were treated with 500 μM sodium caprylate for 24 hours (n = 6 for each group), followed by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 6 for each group). The cells were treated with 5 μM of fenofibrate (Feno) as indicated. E. The cells, as in D, were used to measure β-HB level in culture medium and triglyceride concentration in the cells. F. Wild type and Paqr9-deleted mice were gavaged with corn oil or fenofibrate (10 μg/g body weight) for 5 days and then fasted for 24 hours (n = 4 for mice with corn oil and n = 5 for mice with fenofibrate). The livers of the mice were used in quantitative RT-PCR. G. The mice, as in F, were used to determine β-HB concentration in the serum. H. A graphic summary to depict the inhibitory effect of PAQR9 on HUWE1-mediated poly-ubiquitination and degradation of PPARα protein. Note that PAQR9 competes with PPARα for HUWE1 binding.