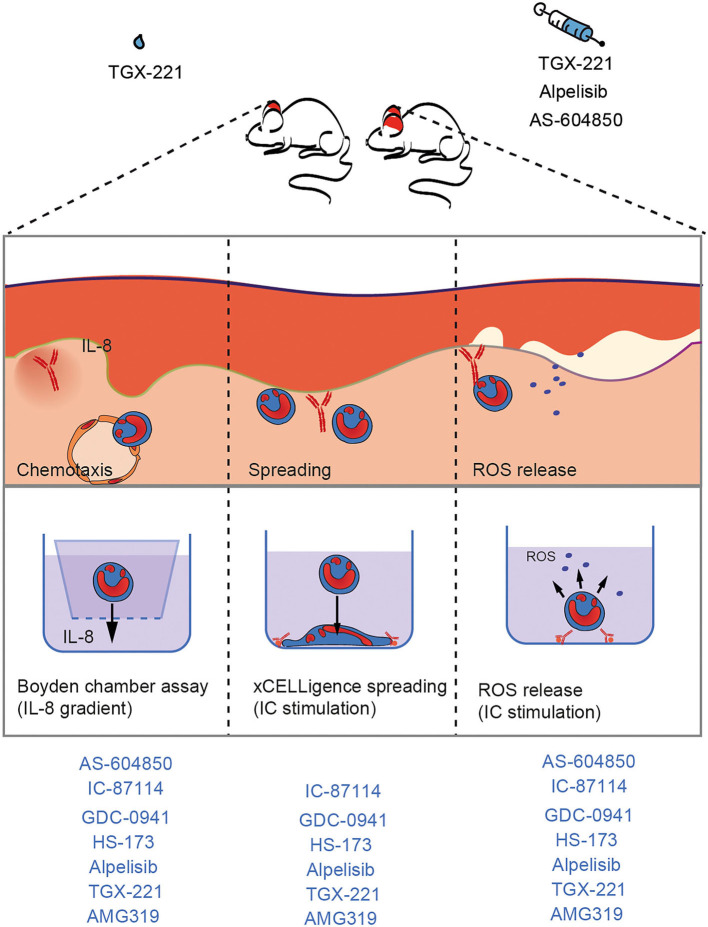
Figure 6.
Unique impact of different PI3K inhibitors on neutrophil-dependent processes in EBA. In the pathogenesis of IC-induced EBA, PMN exert their pathogenic effects in a stepwise manner that is initiated by attracting them into the tissue (chemotaxis), spreading, and adhesion to surfaces of IC deposits and ultimately results in the release of pro-inflammatory substances, such as ROS. As these processes strongly depend to PI3K, inhibition leads to improvement of EBA.