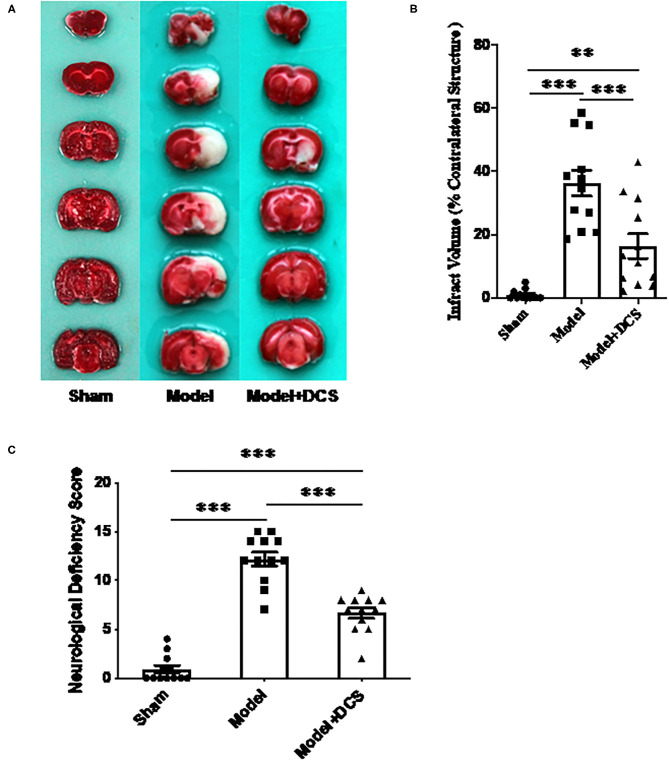
Figure 1.
Effects of deproteinized calf serum (DCS) on neurological dysfunction and infarct volume in the rat model of ischemic stroke. (A) Representative photographs illustrating infarcted regions in the right side of the brain that had not stained with triphenyltetrazolium chloride (unstained areas were defined as infarcted tissue, while normal tissue was stained red). Sham: animals only went through anesthesia with isoflurane until CCA, ECA, lCA, and vagus nerve were exposed and isolated carefully then close the incision. Model + DCS: rats with ischemic stroke administered DCS in normal saline; Model: rats with ischemic stroke administered normal saline (vehicle) only. (B) Statistic analysis for (A). Data shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0005. (C) Neurological dysfunction assessed using the neurological deficiency score (modified Bederson's method). Twelve rats per group were performed. Data shown as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.0005.