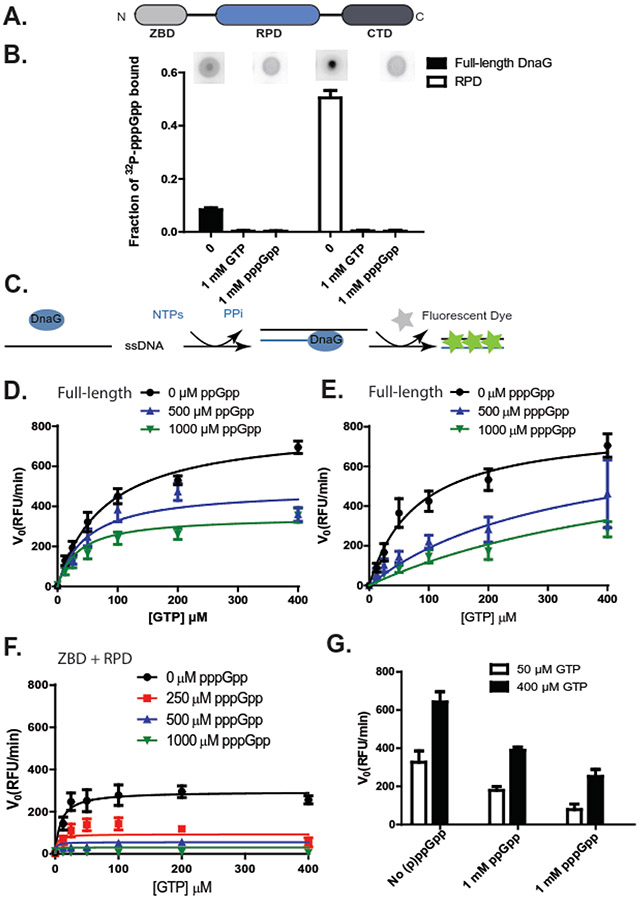
Figure 1. (p)ppGpp, coupled with depletion of GTP substrates, strongly inhibit B. subtilis DNA primase activity.
(A) The bacterial primase DnaG is composed of three domains: an N-terminal zinc binding domain (ZBD), an RNA polymerase domain (RPD), and a C-terminal helicase interacting domain (CTD).
(B) Fraction of [5’-α-32P]-pppGpp bound to 10 μM full-length or RPD-only B. subtilis primase DnaG, with or without single stranded DNA template oJW2384 (ssDNA, 10 μM), GTP (1 mM), or unlabeled pppGpp (1 mM). Representative DRaCALA images are shown above the graph. Error bars represent ± SEM for ≥ 3 replicates.
(C) Schematics of the fluorescence-based primase assay. NTPs are mixed with a ssDNA template and allowed to briefly incubate with or without (p)ppGpp before the addition of primase (DnaG). Aliquots of the reaction are taken at various time points after the addition of DnaG, and DNA-RNA heteroduplexes are measured with a dye that intercalates the double-stranded heteroduplex. The level of fluorescence is dependent upon the quantity of primers synthesized and is reported as relative fluorescent units (RFU).
(D-E) The initial velocity (V0) of full-length DnaG activity at indicated concentrations of ppGpp (D) or pppGpp (E). Reactions were run with 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, or 400 μM GTP. Results are normalized to the enzyme concentration and are reported as relative fluorescent units per minute (RFU/min). Points represent averages of ≥ 3 replicates. Error bars represent ± SEM for ≥ 3 replicates. Curves were fit with an uncompetitive inhibition model for full-length DnaG with ppGpp and a competitive inhibition model for full-length DnaG with pppGpp, based on the highest goodness of fit values (R2). R2 values were obtained by fitting the data to different inhibition modes (Supplemental Figure 1-2).
(F) The initial velocity (V0) of DnaG(ZBD+RPD) activity at indicated concentrations of pppGpp. Reactions were run with 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200, or 400 μM GTP. Results are normalized to the enzyme concentration and are reported as relative fluorescent units per minute (RFU/min). Points represent averages of ≥ 3 replicates. Error bars represent ± SEM for ≥ 3 replicates. Curves were fit with an uncompetitive inhibition model, based on the goodness of fit values (R2). R2 values were obtained by fitting the data to different inhibition modes (Supplemental Figure 3).
(G) Primer synthesis rate by B. subtilis primase at indicated concentrations of GTP and (p)ppGpp (1 mM).