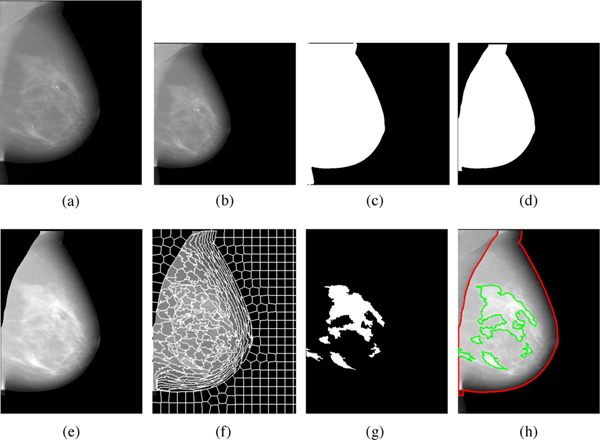
Fig. 2:
Detailed illustration of the Deep-LIBRA algorithm operation. Panel (a) shows the original FFDM image in 16-bit resolution, and panel (b) is the zero-padded image in an 8-bit intensity resolution. The zero-padded image is used by the background segmentation U-Net, which generates the image shown in panel (c). Panel (d) is the output of the module of pectoralis muscle removal using the second U-Net resulting to the final breast segmentation shown in panel (e). The image from panel (e) is used to generate superpixels as shown in panel (f) and perform radiomic feature analysis. Finally, the SVM classifies the superpixels based on the extracted features, resulting in dense tissue segmentation, as shown in panel (g). The panel (h) shows the final dense tissue segmentation overlaid on the original image. Note: The image sizes are different in this figure because the panels (a), (e)-(h) show images in the original image resolution, while the panels (b)-(d) are downsampled images of size 512 × 512 pixels used in U-Net segmentation.