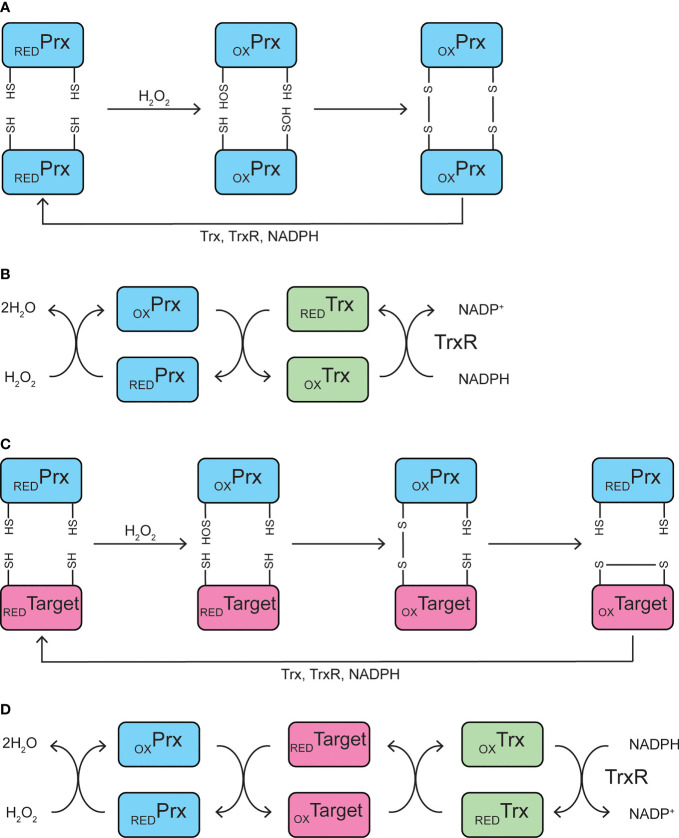
Figure 1.
Catalytic mechanisms. (A, B) Peroxidase mechanism of typical 2-Cys peroxiredoxins. The peroxidatic cysteine residue of peroxiredoxin becomes oxidized to Cys-SOH upon reaction with hydrogen peroxide, which then reacts with the resolving cysteine residue on a neighboring peroxiredoxin to form an intermolecular disulfide bond (A). Peroxiredoxin is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide, and is subsequently reduced by thioredoxin, which becomes oxidized itself and is reduced by thioredoxin reductase, utilizing NADPH (B). (C, D) Potential mechanism of peroxiredoxin-mediated redox relay. The peroxidatic cysteine residue of peroxiredoxin becomes oxidized to Cys-SOH upon reaction with hydrogen peroxide, which then reacts with a redox-sensitive cysteine residue on a target protein to form a mixed disulfide intermediate. The disulfide is transferred to the target protein, resulting in an oxidized target and reduced peroxiredoxin (C). Peroxiredoxin is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide and oxidizes a redox-sensitive target protein. The oxidized target protein is subsequently reduced by thioredoxin, which becomes oxidized itself and is reduced by thioredoxin reductase, utilizing NADPH (D). Prx, peroxiredoxin; Trx, thioredoxin; TrxR, thioredoxin reductase; RED, reduced; OX, oxidized.