FIGURE 5.
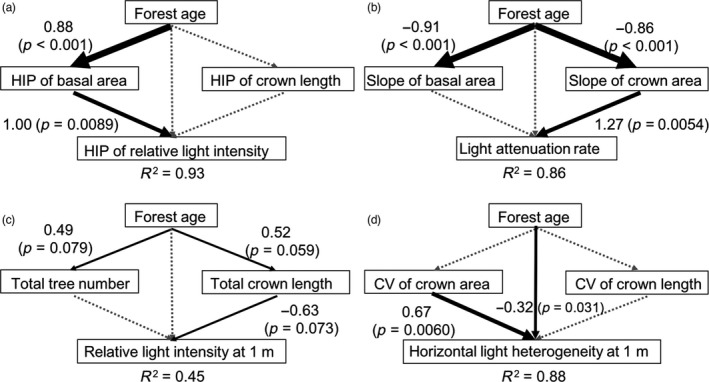
Path models of the standardized effects of forest age on (a) the height of inflection point (HIP) of basal area and crown length, and their effect on the mean HIP of relative light intensity (i.e. the height of 50% cumulative basal area and crown length and relative light intensity), (b) the slope of cumulative basal area and crown area, and their effect on the mean light attenuation rate (i.e. the rate of light extinction), (c) total tree number and total crown length, and their effect on mean relative light intensity at 1 m and (d) coefficient of variation (CV) of forest structural attributes, and their effect on horizontal light heterogeneity at 1 m (expressed as the standard deviation in relative light intensity across 16 subplots at 1 m). Black solid lines indicate significant effects; the values shown next to the arrows are standardized regression coefficients. Grey dotted lines show the full models tested by path models. The thickness of the lines reflects the strength of the effect. The coefficient of determination (R 2) is shown for the final response variable only. In (b), all the variables were log‐transformed to improve normality and homoscedasticity, but the original names are kept for simplicity
