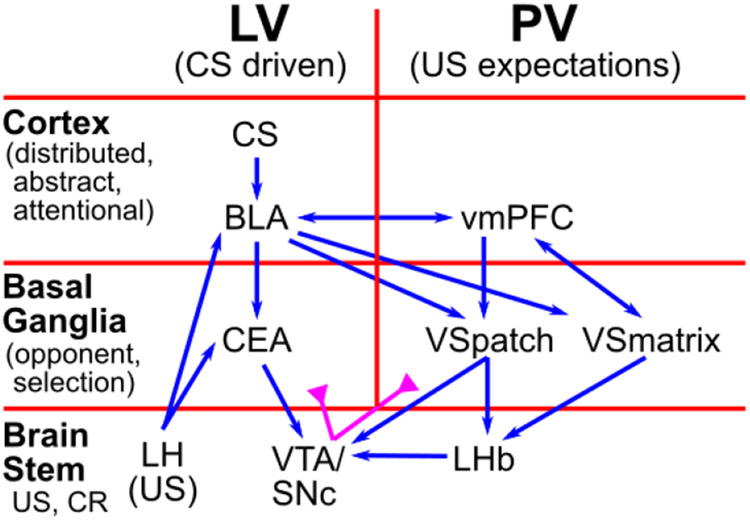
Figure 1:
Overview of PVLV: The main division into LV (learned value) and PV (primary value) cuts across a hierarchy of function in cortical, basal ganglia, and brain stem areas. The cortex provides high-level, abstract, dynamic state representations, and the basolateral amygdala (BLA), which has a cortex-like histology, links these with specific US outcomes. The basal-ganglia-like central amygdala (CEA) quantitatively evaluates the overall evidence for the occurrence of reward or punishment using opponent-processing pathways, and drives phasic dopamine bursts in the midbrain dopamine areas (VTA, SNc) if this evaluation is in favor of expected rewards. BLA also triggers updating of US expectations in ventral / medial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), especially the OFC (orbitofrontal cortex), which then drives another opponent-process evaluation process, in the ventral striatum patch-like areas (VSpatch), the results of which can shunt dopamine bursts for expected US’s, and drive pauses in dopamine firing when an expected US fails to arrive, via projections to the lateral habenula (LHb). Various brain stem areas (e.g., the lateral hypothalamus, LH) drive US inputs into the system, and are also driven to activate conditioned responses (CR’s).