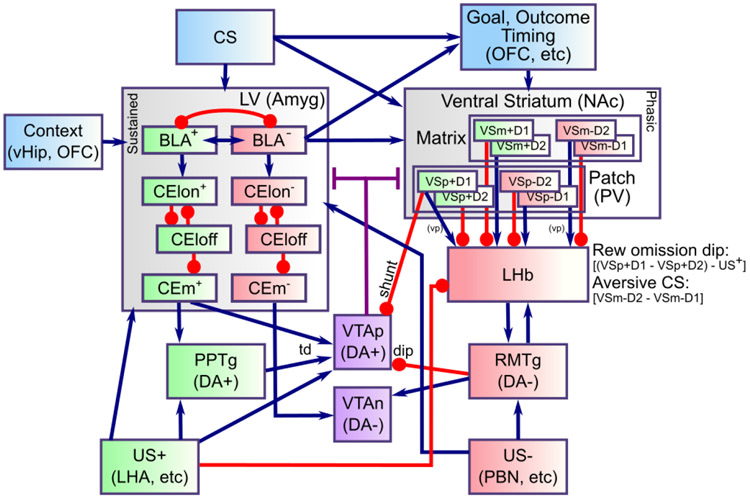
Figure 2:
Detailed components of PVLV, showing the opponent processing pathways within the PV and LV systems, which separately encode the strength of support for and against each US, and with opposite dynamics for appetitive versus aversive valence. BLA has pathways for appetitive and aversive USs, along with distinctions between acquisition and extinction learning, all of which engage in broad inhibitory competition. The BLA projects to central amygdala (CEl, CEm) neurons that integrate the evidence for-and-against a given US, and communicate this net value to the VTA (and SNc, not shown). The ventral striatum (VS) has matrix and patch subsystems, where matrix (VSm) receives modulatory inputs from corresponding BLA neurons and represents CSs in a phasic manner, and patch (VSp) anticipates and cancels USs. Both have a full complement of opposing D1- and D2-dominant pathways, which have opposing effects for appetitive versus aversive USs.