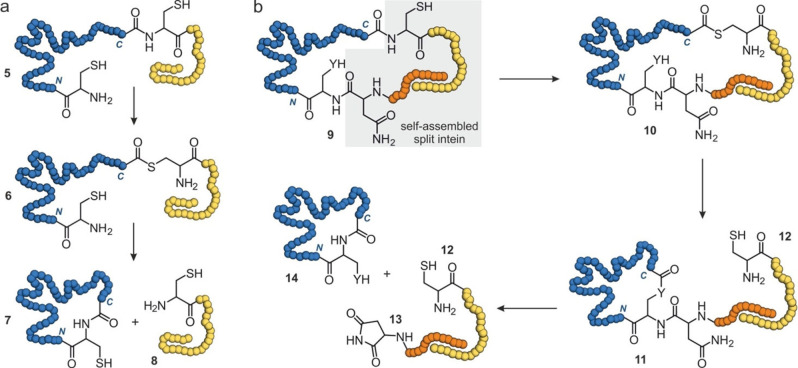
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of intein‐based head‐to‐tail cyclizations (blue: protein of interest): (a) Expressed protein ligation (EPL) involving N‐to‐S acyl transfer to convert an amide bond (5) to a thioester (6). This is followed by trans‐thioesterification with a thiol to release the intein sequence (8, yellow) and subsequent intramolecular native chemical ligation to form the cyclic protein (7). (b) Split intein‐based cyclization first involves assembly of the N‐ and C‐terminal intein fragments (9, orange and yellow), after which an N‐to‐S acyl transfer takes place to form thioester 10. Next, trans‐esterification with an intramolecular nucleophile (Y=S or O) occurs to form a lactone intermediate (11) to release the C‐terminal intein fragment (12). Finally, Y‐to‐N acyl transfer cleaves the N‐terminal intein (13) and forms cyclic protein 14.