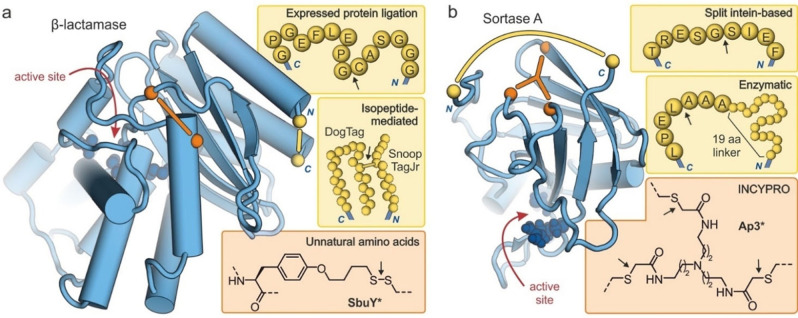
Figure 7.
Structures of cyclized enzymes (blue spheres: active site residues, yellow: protein termini, orange: crosslinking sites). Arrows indicate the ligation site for macrocyclization: (a) Crystal structure of β‐lactamase (TEM‐1, PDB ID 1fqg)[88] showing the introduced modifications resulting from macrocyclizations via EPL (top),[30] isopeptide formation (middle, introduction of 23 and 12 amino acids respectively)[57] and an unnatural amino acid (bottom, disulfide‐bridge between cysteine and tyrosine derivative SbuY at positions 65 and 184, respectively).[71] (b) NMR structure of Sortase A (PDB ID 1ija)[89] showing the introduced modifications resulting from macrocyclizations via a split intein (top),[38] enzymatic ligation (middle, 19‐mer linker sequence: GSSHHHHHHSSGLVPRGSH),[49] and INCYPRO (bottom, with Cys111, Cys149 and Cys177).[50]