Figure 1.
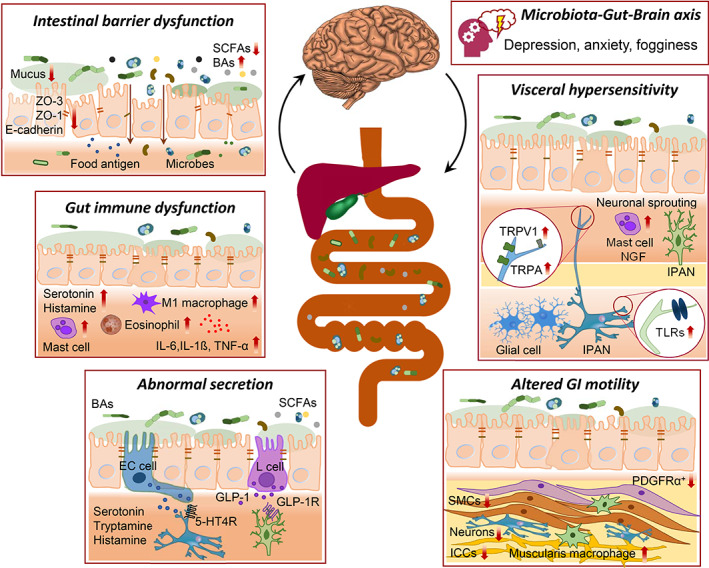
Gut microbiota‐directed pathophysiological mechanisms of functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), currently known as disorders of gut–brain interaction. 5‐HTR, 5‐hydroxytryptamine receptor; BAs, bile acids; E‐cadherin, epithelial cadherin; GLP‐1R, glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor; ICCs, interstitial cells of Cajal; IPAN, intrinsic primary afferent neuron; NGF, nerve growth factor; PDGFRα, platelet‐derived growth factor receptor alpha; SCFAs, short‐chain fatty acids; SMCs, smooth muscle cells; TLRs, toll‐like receptors; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐alpha; TRPA1, transient receptor potential ankyrin 1; TRPV1, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1; ZO, zonula occludens.
