Figure 2.
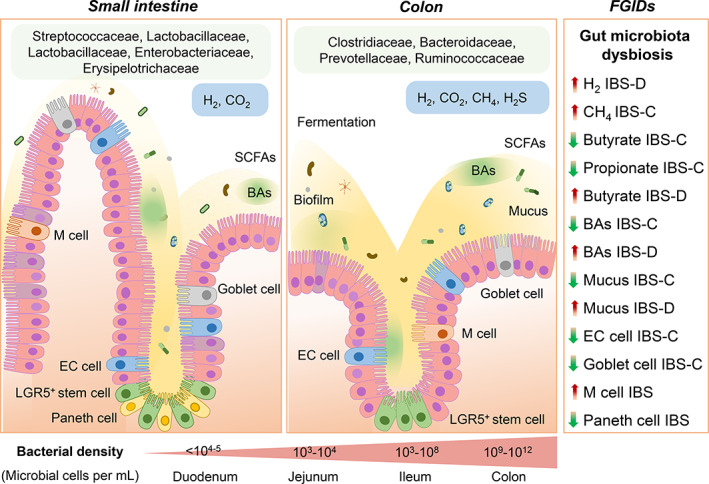
Pathophysiological mechanisms of functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), currently known as disorders of gut–brain interaction. BAs, bile acids; CH4, methane; EC cell, enterochromaffin cell; H2, hydrogen; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; IBS‐C, constipation‐predominant irritable bowel syndrome; IBS‐D; diarrhea‐predominant irritable bowel syndrome; LGR5+, leucine‐rich repeat‐containing G‐protein coupled receptor 5; M cell, microfold cell; SCFAs, short‐chain fatty acids.
