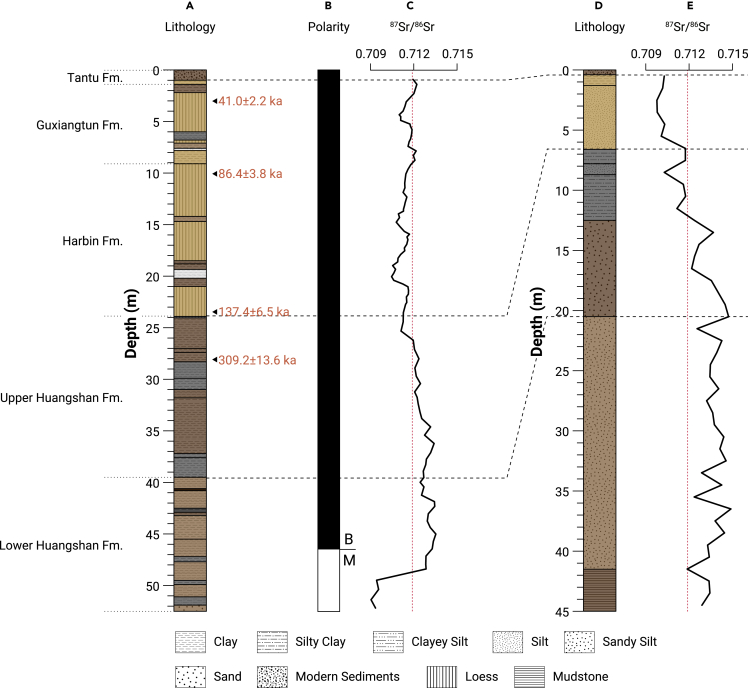
Figure 4.
Stratigraphic correlations and the Sr isotopic ratios of the sediments from the Huangshan section, Huangshan core, and Dongjiang core
(A and B) Lithostratigraphy and Paleomagnetic polarities from the Huangshan section, based on the data from Wang et al.4
(C) Sr isotopic ratios from the Huangshan core, data from Wei et al.5
(D and E) Lithostratigraphy and Sr isotopic ratios from the Dongjiang core, data are from this research. The Dongjiang Bridge core was drilled at 45°50′28″N, 126°36′27″E. The sedimentary sequence of the Dongjiang core from the top to the unconformity with the Mesozoic includes nine layers: (1) modern sediments, 0.4 m; (2) yellowish-brown, alluvial fine muddy silt, 0.9 m; (3) yellowish-brown alluvial silt, 5.3 m; (4) gray to dark gray, static water deposition, sludge-like mud, 1.2 m; (5) dark gray alluvial fine silt, 0.9 m; (6) dark gray, static water deposition, sludge-like mud, 3.8 m; (7) grayish-brown, fluvial sand, including ~3% of gravels, gravel diameter ~3 mm, 8 m; (8) grayish-brown alluvial medium grained sandy silt, 21 m; and (9) grayish-brown, mudstone, with parallel bedding, 3.5 m. The unconformity is between layer 8 and layer 9. The age in red is the OSL date. The red dashed lines indicate the Sr isotope ratio of the sediments adhering in the Harbin cranium.