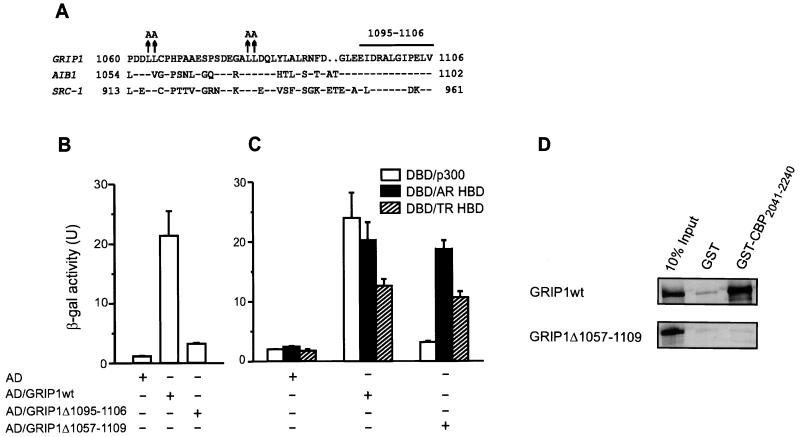
FIG. 7.
Mapping the p300/CBP binding site (AD1) of GRIP1. (A) Sequence of the core p300/CBP binding region of p160 coactivators. Amino acids identical to those in GRIP1 are indicated (−), as are gaps introduced for optimal sequence alignment (. .). Previously characterized mutations (↑) (25, 55) and a new deletion (horizontal bar) described here are shown above the GRIP1 sequence. (B and C) Binding of wild-type and mutant GRIP1 to p300 and NR HBDs. Yeast two-hybrid assays were conducted as in Fig. 1B. AD, Gal4 AD; DBD, Gal4 DBD. (D) Binding of wild-type or mutant GRIP1 to a C-terminal fragment of CBP in vitro. Wild-type or mutant GRIP1 was translated in vitro from a pSG5.HA vector, and binding to GST-CBP2041–2240 was measured as in Fig. 3.