FIGURE 1.
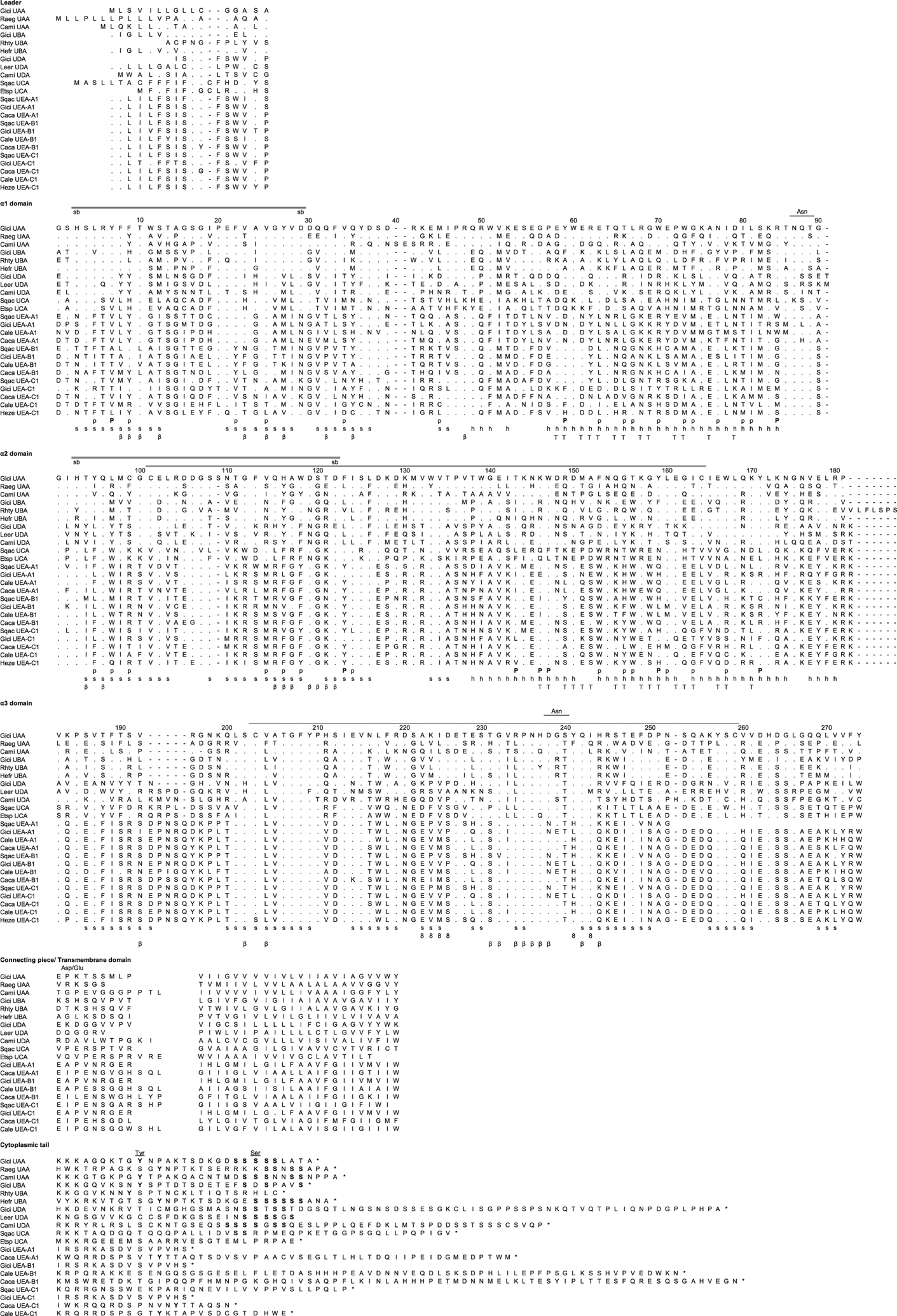
Amino acid alignment of the representative MHC class I lineages in cartilaginous fish, UAA, UBA, UCA, UDA, and the new multicopy lineage UEA. GenBank accession numbers are listed in Supplemental Table II. Dashes indicate gaps, and asterisks indicate the stop codon. s and h indicate the β strands and α helices, and the line connecting the two Cys (C) in the α2 and α3 domain indicates the class I canonical disulfide bridge. The double line between the amino acids His (H) and Asp (D) indicates the possible salt bridge, whereas eight β and T indicate the residues that are potential binding with CD8, β2m, and TCR, respectively. P marks the invariant residues that bind to the N and C termini of the bound peptide in the classical class I molecules, and p indicates the other 28 potential conserved peptide binding residues. The Asn (N) marks the asparagine-linked glycosylation site, and Asp/Glu (D/E) indicates the typical aspartic acid and glutamic acid residues found in the CP (light shade). The underlined Asn above the a3 domain in Fig. 1 denotes a potential glycosylation site for some UEA sequences. Because of the high diversity in the CYT, the alignment would be merely speculative. The numbering of amino acid positions is based on human HLA-A2.
