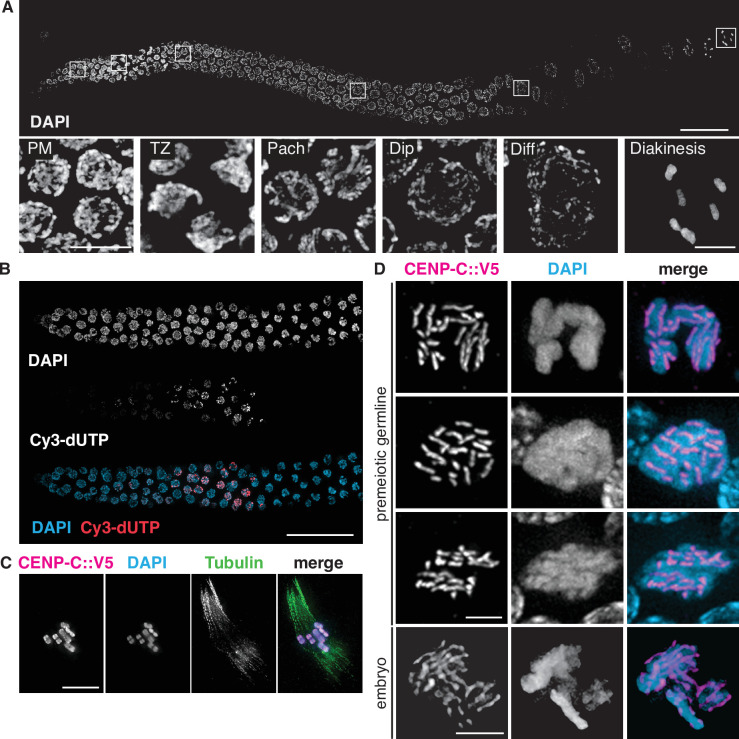
Figure 1. Germline organization and meiotic nuclear morphology in P. pacificus are superficially similar to C. elegans.
(A) Projection image of the distal arm of a P. pacificus hermaphrodite gonad stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 30 μm. Insets show representative nuclei from the premeiotic region (PM), transition zone (TZ), pachytene (Pach), diplotene (Dip), diffuse stage (Diff), and diakinesis. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Distal region of a P. pacificus germline following injection of fluorescent nucleotides to label replicating DNA. Scale bar, 30 μm. (C) Metaphase I oocyte expressing CENP-C::V5, stained with anti-V5, DAPI, and anti-tubulin. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Mitotic chromosomes (DAPI) in the premeiotic germline of adult hermaphrodites and a 2–4 cell stage embryo and expressing CENP-C::V5 (magenta). Scale bar, 2 μm.