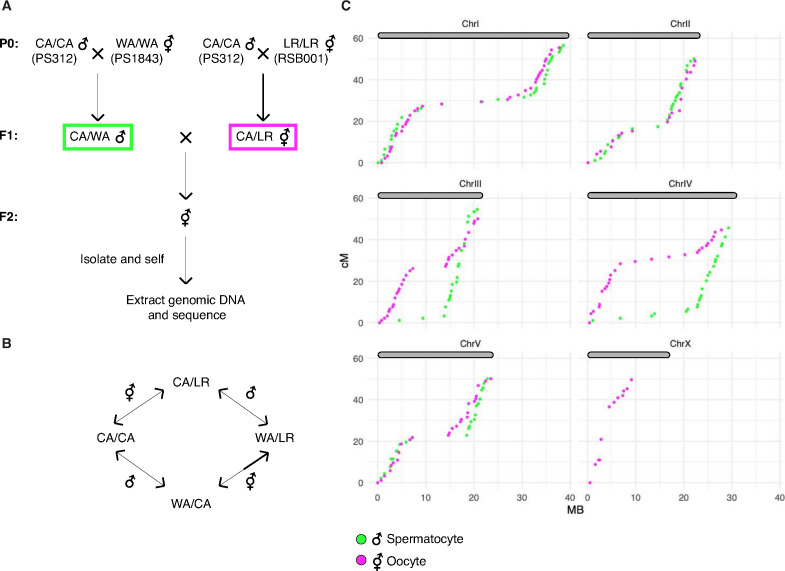
Figure 8. A genetic map for Pristionchus pacificus based on recombination in inter-strain hybrids.
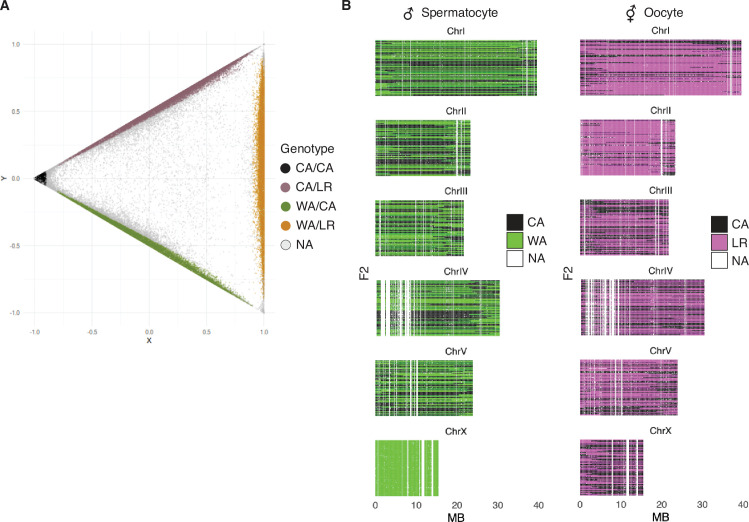
(A) Crossing scheme to generate a recombination map using three parental strains. California PS312 (CA), Washington PS1843 (WA), and La Réunion Island RSB001 (LR) strains were crossed to obtain F1 hybrids, which were then crossed to each other. Whole-genome sequencing of progeny from crosses between hybrid F1s enabled the analysis of meiotic recombination events in each F1 parent. (B) Genotype transitions along a chromosome in F2 correspond to recombination in the male or hermaphrodite F1 parent. (C) Marey plots show genetic map position in centimorgans vs. the physical position in megabases for male (green) and hermaphrodite (magenta) meiosis. Each bin was treated as a single locus and dots were plotted at the center of each marker bin. Map positions were computed with OneMap as described. The observed map length of ~50 cM indicates that chromosomes undergo an average of one crossover (CO) per meiosis. The X chromosome lacks a homolog in males, so there is no male-specific map for the X in our data. See also Figure 8—figure supplement 1 and Figure 8—source data 1.