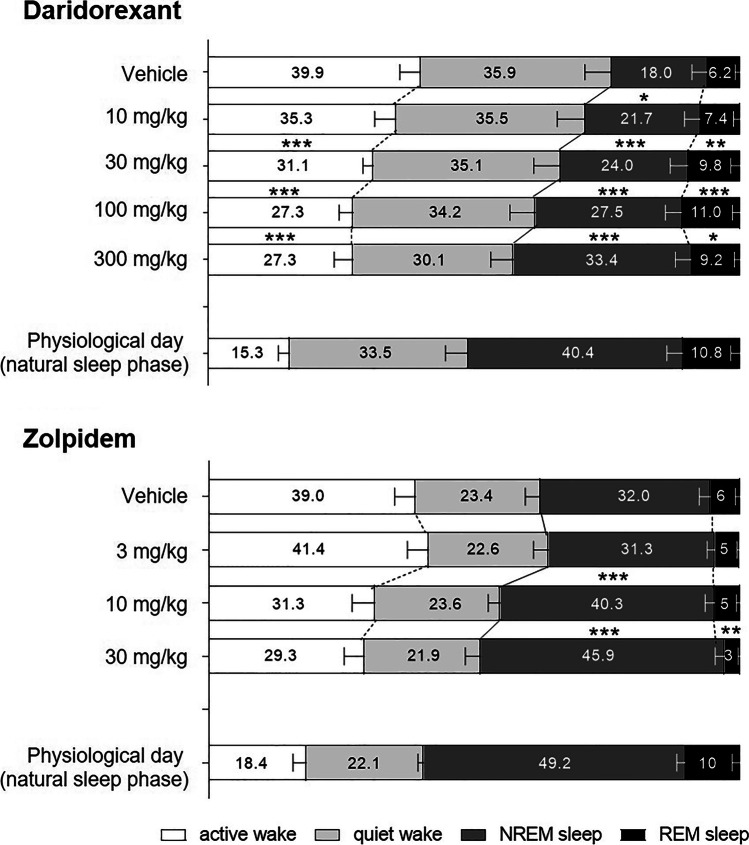
Fig. 2.
Effect of daridorexant and zolpidem on sleep and wake stages and sleep architecture during the first 6 h of the night active period in rats. Drugs were administered as single dose by oral gavage at the beginning of the dark phase. Daridorexant was formulated in a vehicle of 0.5% methyl cellulose (MC) and zolpidem in a vehicle of 0.25% MC. Values represent the percentage of time spent in each wake and sleep stage over the first 6 h of the active, night period. Physiological day values represent the first 6 h of the normal inactive, daytime period (physiological sleep period for nocturnal rats) of the respective vehicle-treated rat groups. Data are expressed as mean + standard error of the mean. One-way ANOVA was performed separately for each parameter, followed by the post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated rats. Each dose–response (daridorexant, and zolpidem) represents independent crossover studies with n = 8 male Wistar rats. MC, methylcellulose; REM, rapid eye movement; NREM, non-REM. ANOVA, analysis of variance. Full experimental details provided by Boss et al. 2020. Daridorexant dose response: Boss et al. The quest for the best dual orexin receptor antagonist (daridorexant) for the treatment of insomnia disorders. ChemMedChem 2020; 15:2286–2305. Copyright Wiley–VCH GmbH. Reproduced with permission. Zolpidem dose response: data-on-file