Figure 1.
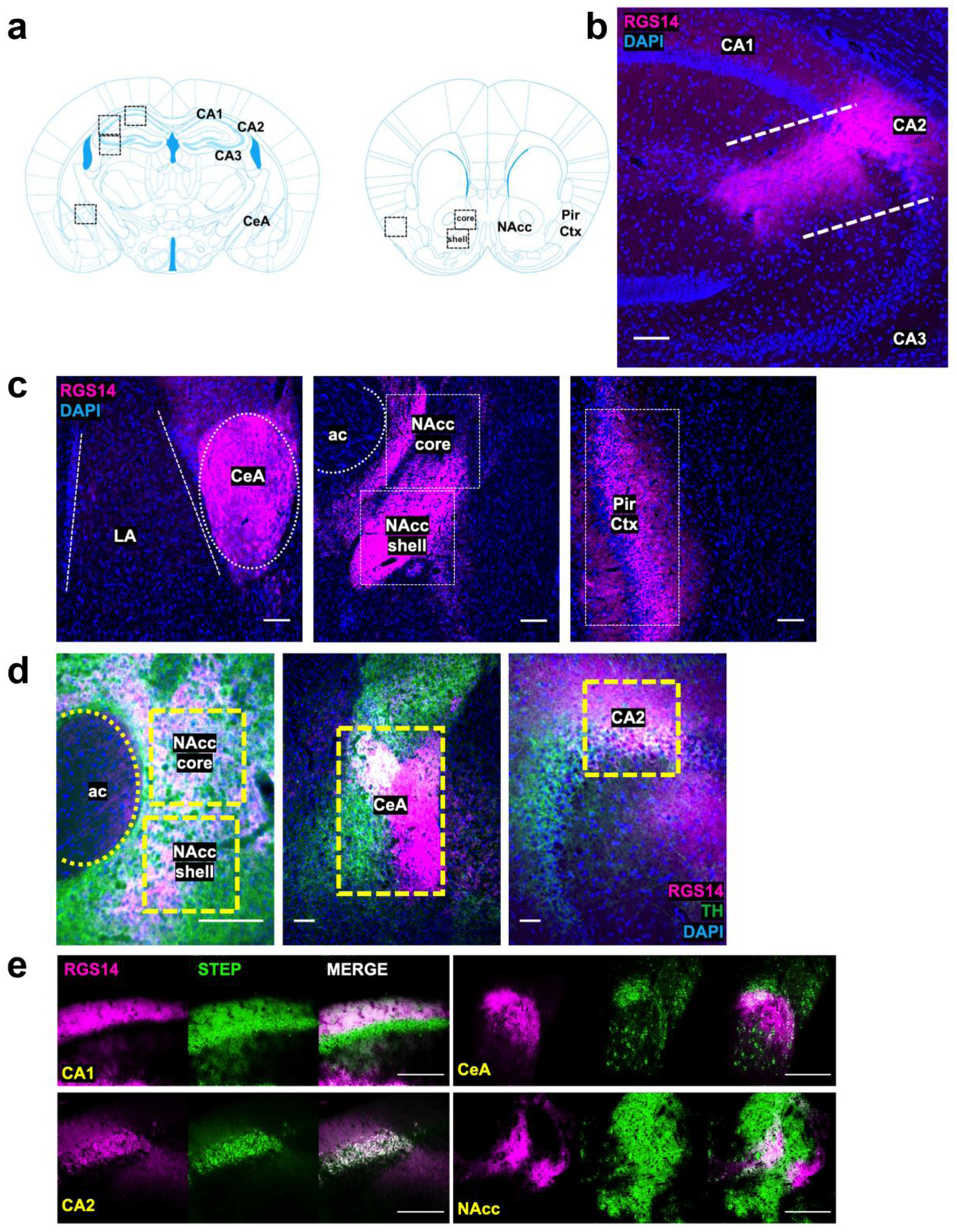
Detection of RGS14 immunoreactivity (RGS-ir) in cortical and limbic structures of the mouse brain. a Brain regions selected for immunohistochemical analysis of endogenous RGS14-ir, as well as c-fos and pERK induction following exposure to novelty and cocaine. b RGS14 (magenta) is endogenously expressed in the dorsal hippocampus Cornu Ammonis (CA) CA1 and CA2 subfields, but not in subfield CA3. c RGS14-ir can also be detected in central amygdala (CeA), nucleus accumbens (NAcc) core and shell subregions, and piriform cortex (Pir Ctx). The anterior commissure (ac) is depicted to delimit the NAcc, and the lateral amygdala (LA) is depicted to distinguish the boundaries of the CeA. d RGS14-ir neurons (magenta) in the NAcc, CeA, and dorsal hippocampus are densely innervated by catecholaminergic terminals, visualized by immunostaining for the catecholamine synthetic enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH; green). e RGS14-ir neurons overlap with the molecular marker Striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) in CA1, CA2, CeA, and NAcc. Scale bars denote 100 μm.
