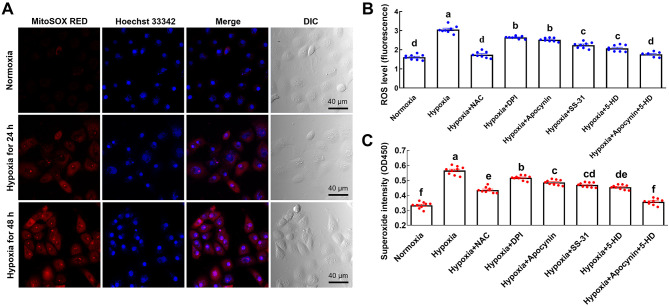
Figure 2.
Hypoxia-induced excessive ROS is mainly derived from mitochondrial ETC and NOX pathways
A: Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of mitochondrial superoxide levels (red) in LYCF cells with/without hypoxia for 24 and 48 h. B: Fluorescence microplate reader measurement of changes in intracellular ROS levels (fluorescence OD value) in LYCF cells with/without hypoxia and/or NAC, DPI, apocynin, SS-31, 5-HD, or their combination for 24 h. C: Superoxide assay of intracellular superoxide levels in LYCF cells with/without hypoxia and/or NAC, DPI, apocynin, SS-31, 5-HD, or their combination for 24 h. Different letters on bars represent statistically significant intergroup differences.