Figure 7.
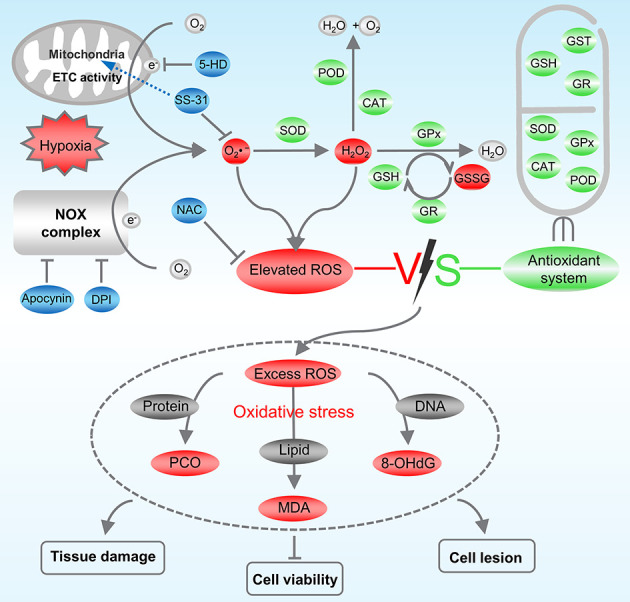
Regulation mode of ROS inhibitor on redox homeostasis in Larimichthys crocea under hypoxic stress
Hypoxia induces L. crocea to produce excessive O2•- through mitochondrial ETC and NOX complex pathways. O2•- is reduced to H2O2 by SOD enzymes, H2O2 is reduced to H2O and O2 by CAT and POD enzymes and reacts with GSH substrate and GPx enzymes to produce GSSG. GR is responsible for reduction in GSSG to GSH to continue its antioxidant action. Antioxidant defense system is activated but fails to remove excessive ROS in time, which attacks proteins, lipids, and DNA in the organism, triggering oxidative stress and causing tissue and cell damage. Apocynin and DPI prevent ROS production by inhibiting NOX complex. SS-31 enters mitochondrial inner membrane to specifically scavenge mitochondrial ROS. 5-HD inhibits production of mitochondrial ROS by specifically inhibiting mitoK ATP.
