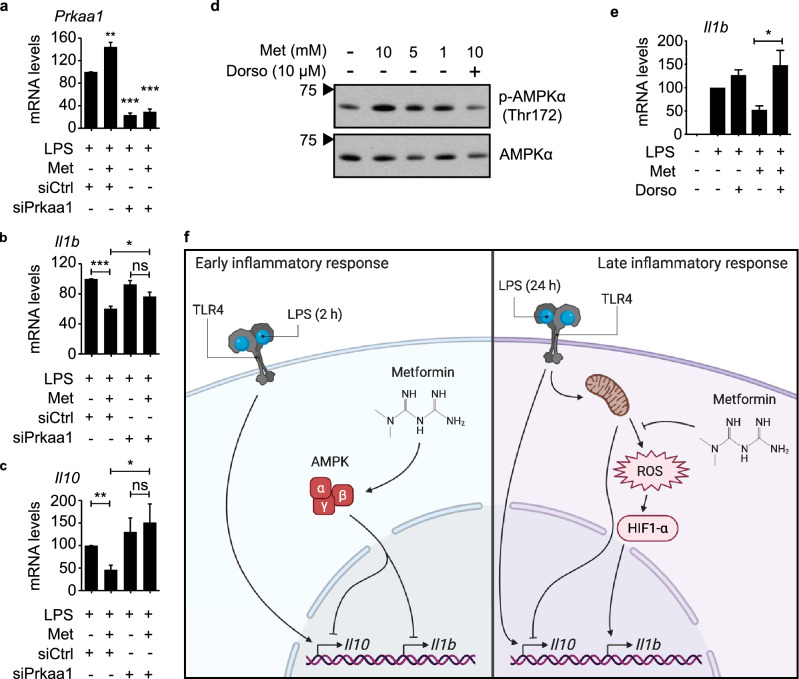
Figure 2.
Metformin alters transcript levels during the acute LPS response by activating AMPK. (a–c) RT-qPCR with RNA from RAW 264.7 cells, quantifying expression of the indicated genes. Cells were transfected with siRNA targeting Prkaa1 (siPrkaa1) or a control siRNA (siCtrl), pretreated or not with 5 mM metformin (Met) for 6 h, and stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS for 2 h. Rplp0 served as reference gene. (d) Western blot of lysates from primary BMDMs treated with metformin (Met) and dorsomorphin (Dorso) for 6 h, probing for phospho-AMPKα (Thr172) and total AMPKα. Black arrows indicate molecular weight in kDa. Images were cropped. See Supplementary Fig. S1j,k for full lanes. (e) RT-qPCR with RNA from J774 cells, quantifying expression of Il1b. Cells were pretreated with 5 mM metformin (Met) and/or 10 μM dorsomorphin (Dorso) for 6 h, followed by stimulation with 100 ng/ml LPS for 2 h. Tubb5 served as reference gene. (f) Model of the mechanism through which metformin affects the inflammatory response of macrophages. During the early phase, metformin reduces the transcription of Il1b and Il10 by activating AMPK (left panel). During the late phase, metformin reduces the production of ROS by mitochondria, which limits protein levels of HIF1-α and results in decreased expression of Il1b, whereas expression of Il10 is enhanced (right panel). p-values: ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; ns not significant. Error bars indicate standard error of 5 independent experiments.