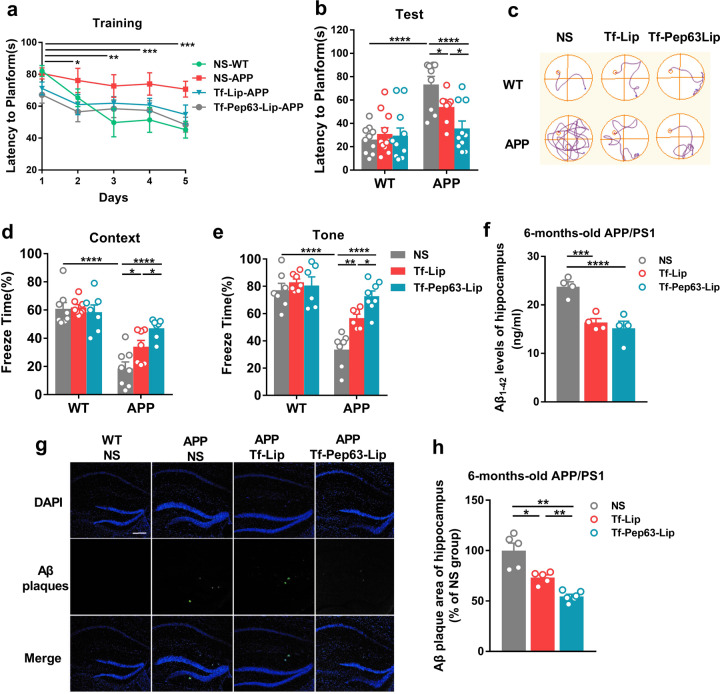
Fig. 2. Tf-Pep63-Lip and Tf-Lip rescue memory deficits and decrease Aβ1-42 levels in APP/PS1 mice.
Six-month-old APP/PS1 and WT mice were treated with Tf-Lip or Tf-Pep63-Lip at a lipid dose of 5 mg/kg intravenously every other day for 30 days or treated with the same volume of 0.9% NS as negative controls. a Escape latency was significantly reduced after training compared with the first day (n = 10). b APP/PS1 mice injected with Tf-Pep63-Lip and Tf-Lip took less time to reach the platform than NS-treated mice (n = 10). c Representative swimming path on the testing day. d, e Tf-Pep63-Lip and Tf-Lip improved impaired context-dependent (d) and tone-dependent (e) fear memory in APP/PS1 mice compared with NS-treated APP/PS1 mice (n = 8). f Both Tf-Pep63-Lip and Tf-Lip remarkably decreased Aβ1-42 levels in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice, as measured by ELISA (n = 4). g Representative immunofluorescence images of Aβ1-42 plaques (green) in hippocampal brain sections of APP/PS1 mice treated with 0.9% NS, Tf-Lip, or Tf-Pep63-Lip at a lipid dose of 5 mg/kg intravenously. h The area of Aβ1-42 plaques was quantified and normalized to NS-treated APP/PS1 mice. Tf-Lip and Tf-Pep63-Lip significantly decreased the area of Aβ1-42 plaques in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice (n = 5). Scale bar: 200 µm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, significantly different. Data are presented as means ± SEM.