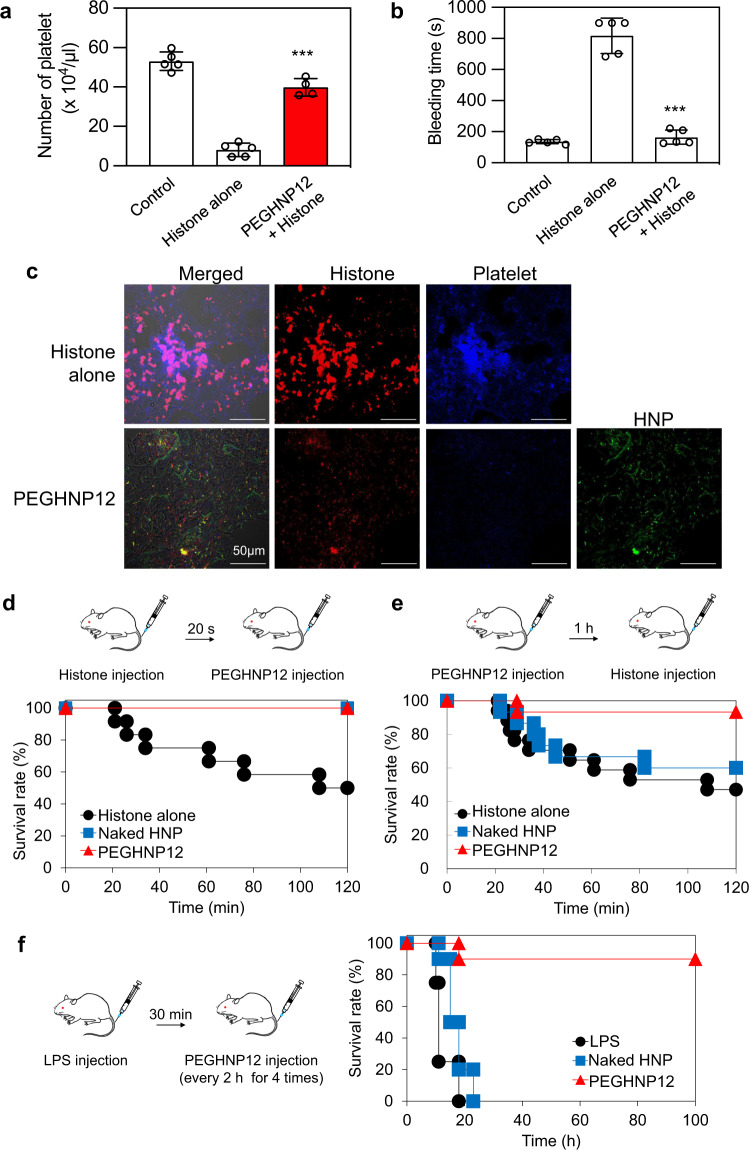
Fig. 6. Protection of mice from septic lethality by HNPs in vivo.
a Number of platelets after injecting histones and/or HNPs. Histones (40 mg/kg) were injected into mice 1 h after injecting HNPs (10 mg/kg). Twenty minutes after the injection, the number of platelets was measured. Significant difference; ***p < 0.0001 vs. Histones alone. Data represent the means ± s.d. n = 4–5. Data represent the means ± s.d. n = 4. Differences within a group were evaluated by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test. b Tail bleeding time after injecting histones and/or PEGHNPs. Histones (40 mg/kg) were injected into mice 1 h after injecting HNPs (10 mg/kg). Twenty minutes after the injection, the time of bleeding from the tail was measured. Significant difference; ***p < 0.0001 vs. Histones alone. Data represent the means ± s.d. n = 4–5. Data represent the means ± s.d. n = 4. Differences within a group were evaluated by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test. c Immunostaining of lungs after injecting histones and/or HNPs. Cy5-histones (40 mg/kg) were intravenously injected into mice 1 h after FITC-PEGHNP injection (10 mg/kg). Twenty minutes after the histone injection, the frozen section of the lungs was stained with CD41. Red: histones; blue: platelets; green: HNPs. Bar: 0.05 mm. d Survival rate of mice intravenously treated with PEGHNPs (10 mg/kg) at 20 s after the injection of histones (75 mg/kg). e Survival rate of mice intravenously treated with histones (75 mg/kg) at 1 h after the injection of PEGHNPs (10 mg/kg). f Survival rate of LPS-induced (15 mg/kg) sepsis model mice improved by the injection of PEGHNP12 (10 mg/kg). LPS lipopolysaccharide.