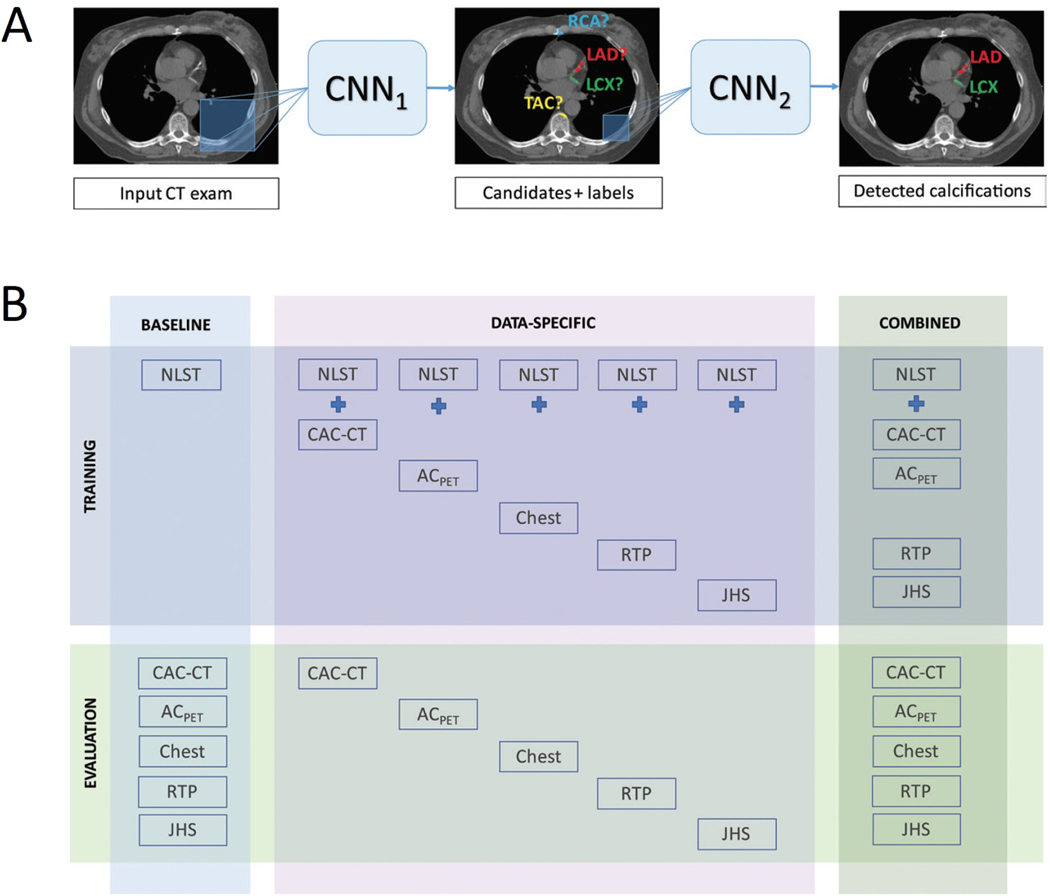
Figure 2. Automatic coronary artery calcium scoring using deep learning.
(A) The deep learning algorithm consists of two convolutional neural networks (CNNs): the first CNN detects candidate calcifications by voxels with attenuation of greater than 130 Hounsfield units and assigns them to a coronary artery; while the second CNN detects true calcified voxels among candidates detected by the first CNN. (B) The baseline algorithm was trained with National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) scans, and its performance was evaluated in each CT protocol type. Five data-specific algorithms were trained, according to CT protocol type, and evaluated in the respective CT type. The combined algorithm was trained and evaluated using all available CT protocol types. CT types used for training were NLST CT scans, coronary artery calcium scoring CT (CAC-CT), PET attenuation correction CT (ACPET), diagnostic chest CT, radiation therapy treatment planning (RTP) CT, and Jackson Heart Study (JHS) CT scans. Reproduced with permission from van Velzen et al.32. LAD = left anterior descending artery; LCX = left circumflex artery; RCA = right coronary artery; TAC = thoracic aorta calcification.