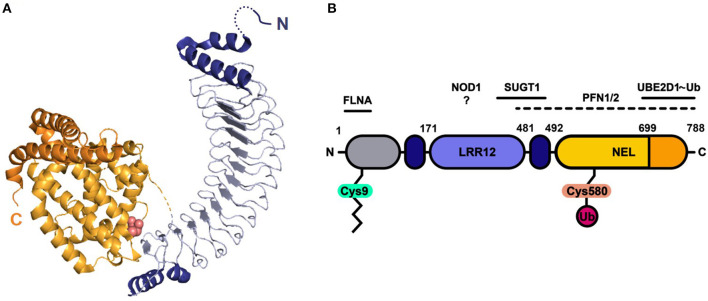
Figure 1.
Protein structure and domain architecture of S. Typhimurium effector SspH2. (A) The ribbon diagram represents the by X-ray crystallography solved protein structure of SspH2 residues 166-783 (PDB 3G06), consisting of two main domains: the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain (blue) and the novel E3 ligase (NEL) domain (orange). Both sides of the 12 LRRs are capped with alpha helices (dark blue). The NEL domain harbors the catalytic Cys residue (pink atoms shown in spheres) and can be further subdivided into a globular domain (light orange) and a 2-helical C-terminal extension (dark orange). (B) A linear representation of the SspH2 architecture and its reported host interactors ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 D1 (UBE2D1), suppressor of G2 allele of SKP1 homolog (SUGT1), nucleotide binding oligomerization domain containing 1 (NOD1), profilin 1 (PFN1) and 2 (PFN2) and filamin-A (FLNA). SspH2 is S-palmitoylated (zigzag line) at Cys9, attaching the effector to the host membrane. As an E3 ubiquitin (Ub) ligase, catalytic Cys580 of SspH2 is involved in the transfer of Ub to substrate proteins. Color-coding of domains is done according to panel (A). Gray region represents sequence not covered in the crystal structure.