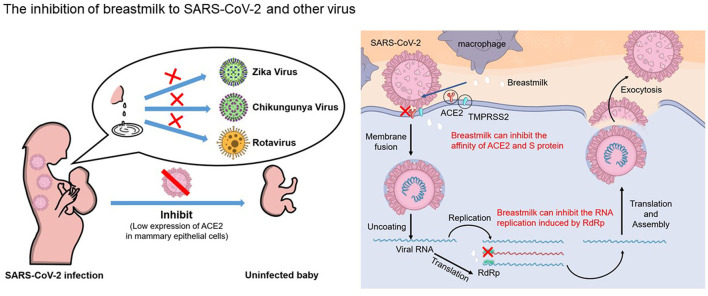
Figure 1.
Human breastfeeding should be encouraged for the mothers who are suspected or confirmed with COVID-19. Breast milk provide protection against several pathogens including Zika virus, chikungunya virus and rotavirus; for SARS-CoV-2, breast milk not only block the binding between ACE2 and spike protein, but also potently inhibit RdRp activity of SARS-CoV-2. The antiviral effects of breast milk and low levels of ACE2 expression in the breasts could explain that breast-fed newborns are less likely to be infected with virus from their COVID-19 mothers through breast milk.