Figure 4.
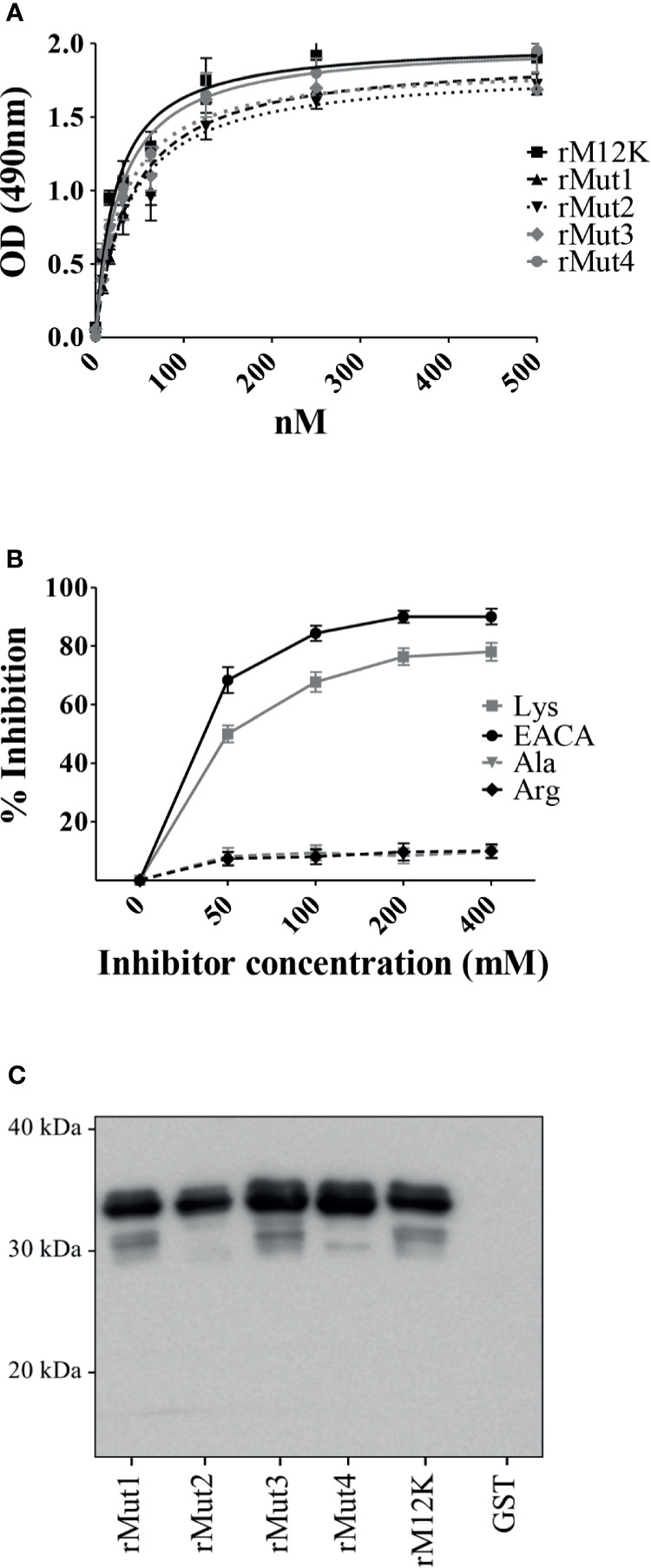
Lysine residues in the MK-rich domain are not involved in Plg binding. (A), Binding of M12K and its mutated forms to Plg. Recombinant M12K and its mutated forms (250 nM) were immobilized on the surface of microtiter wells, and their binding was tested with increasing concentrations of Plg. Bound Plg was detected with rabbit anti-Plg antibodies and HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. (B), Selective inhibition of Mut4-Plg interactions. Competitive ELISA assays were done with immobilized rMut4 (250 nM) to which Plg (100 nM) was added in the presence of the indicated concentrations of (EACA) or L-lysine (Lys). L-alanine (Ala) and L-arginine (Arg) were used as negative controls. Inhibition ability is shown as percentage. Data are means ± SD from three independent experiments conducted in duplicate. (C), Western blot analysis of binding to Plg of M12K and its mutated forms. Recombinant M12K or its mutated forms were loaded onto SDS-PAGE (5µg/lane), transferred to nitrocellulose membrane and probed with Plg (1µg/ml). Bound Plg was detected using a primary polyclonal anti-Plg antibody followed by secondary HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. GST was used as negative control. Numbers indicate the molecular mass of protein standards in kDa. Shown are data from one representative experiment of two producing similar results.
