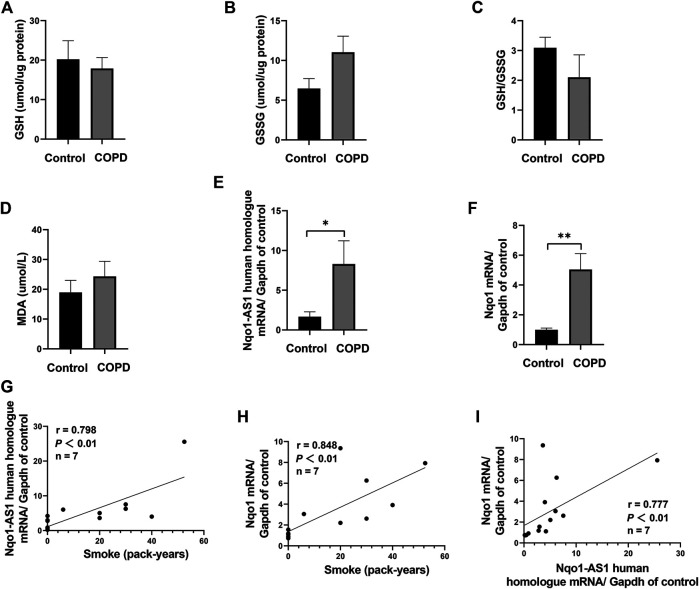
FIGURE 2.
Nqo1-AS1 human homologue is both positively correlated with smoking amount and Nqo1 mRNA expression in patients with COPD. Levels of reduced glutathione (GSH) (A), Glutathione disulfide (GSSG) (B), GSH/GSSG ratio (C) and MDA (D) were assessed in serums from patients with COPD and healthy controls. Expressions of Nqo1-AS1 human homologue (E) and Nqo1 mRNA (F) were examined in PBMCs from patients with COPD and healthy controls (*p<0.05; **p <0.01). Both Nqo1-AS1 human homologue (G) and Nqo1 mRNA (H) expressions were positively correlated with smoking amount of patients with COPD. (I) The expression levels of Nqo1-AS1 human homologue and Nqo1 mRNA in PBMCs from patients with COPD and healthy controls were positively correlated with each other (n = 7/group; p <0.01; r represents spearman correlation coefficient). Nqo1-AS1 is positively correlated with Nqo1 mRNA expression in lung tissue of mice exposed to CS.