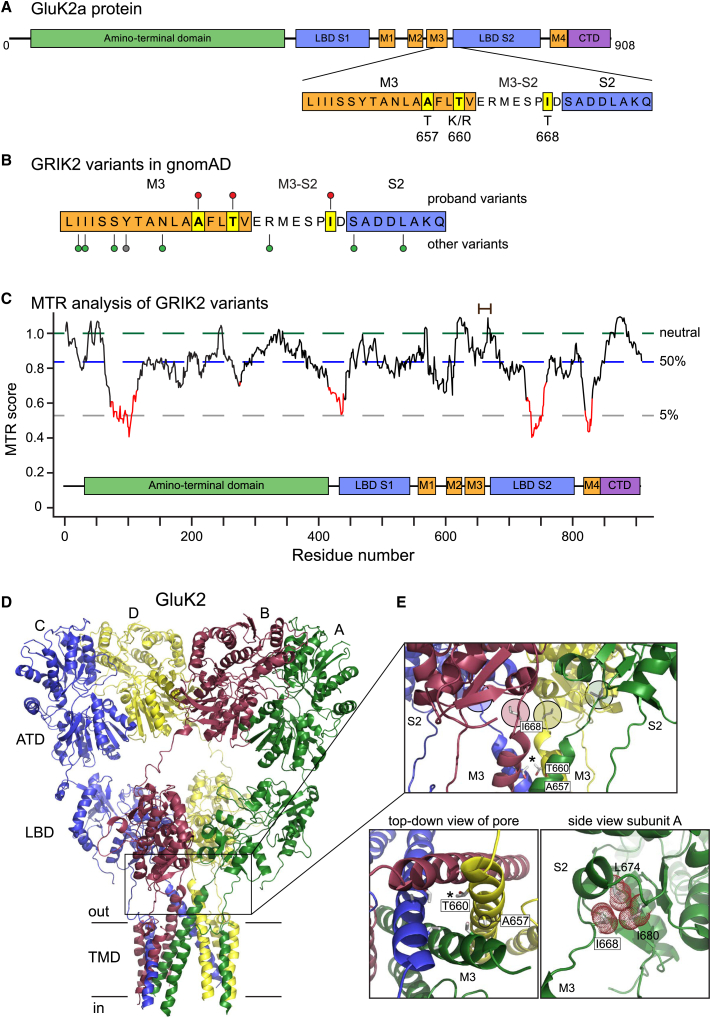
Figure 2.
Mapping of GRIK2 variants onto protein structures and analysis of tolerance ratios
(A) The primary sequence and key structural domains of the GluK2 subunit are shown in cartoon form together with the predicted divergences from wild-type amino acids.
(B) Lollipop mapping of the sites of variants in this report (red lollipops), other missense variants (green), and a truncating variant (gray) in the “hotspot” region in the M3 helix and M3-S2 linker domains.24 Variant sites are from gnomAD.
(C) Missense tolerance ratio of GRIK2 variants analyzed with a 31 amino acid window. Red domains indicate highly intolerant regions of the gene mapped onto the primary protein sequence. The relative positions of the variants in this study are shown with a brown bar at the top.
(D) Tetrameric structure of the homomeric GluK2 KAR (PDB: 5kuf);26 each subunit is color-coded and denoted as A, B, C, or D according to convention.27 The boxed region harbors the protein variants and spans the bottom of the LBDs, the gating linkers, and external segments of the pore helices.
(E) The top box shows a side-on view of isoleucine 668 (I668) in the M3-S2 linker (circled, colored by chain) and threonine 660 (T660) in M3 (starred). Alanine 657 (A657) projects into neighboring M3 helices and is not visible in this view. The top-down view of the M3 helices reveals the projection of threonine side chains into the channel pore (asterisk marks threonine 660 in chain D). Alanine 657 stabilizes interactions between M3 domains (circled in chain D). A closer view of isoleucine 668 with the atomic surface shown as red dots illustrates the projection of its hydrophobic side chain into a pocket formed from residues in the S2 domain of the LBD. ATD, amino-terminal domain; CTD, carboxy-terminal domain; LBD, ligand-binding domain; MTR, missense tolerance ratio; TMD, transmembrane domain.