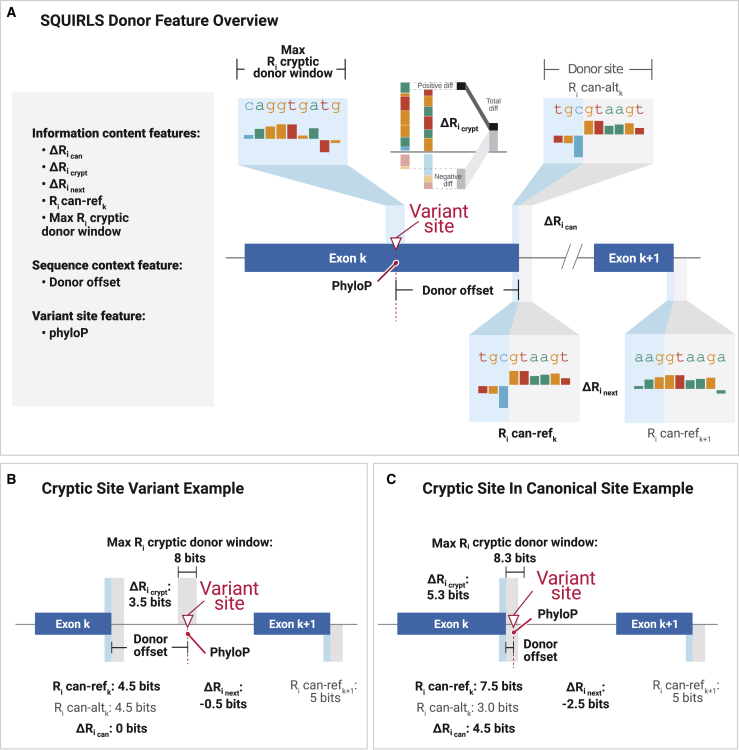
Figure 2.
Calculation of features for the donor site
(A) SQUIRLS calculates seven features to evaluate variant impact on the donor site. The individual information content of the reference and alternate canonical splice site and of the donor site in the following exon (Exon ) are calculated and used to determine the difference in information content between the reference and alternate canonical splice site , the difference between the best candidate cryptic splice site and the alternate sequence of the canonical splice site , and the difference between the donor site at exon k and k+1, because differences in splice site strength can be predictive of exon skipping.14 See Table 1 for information about other features.
(B) In this example, a variant in intron k creates a cryptic splice site with 8 bits, which is greater than the individual information of the canonical splice site (4.5 bits), so = 3.5 bits. The variant does not change the sequence of the canonical splice site, so = 0. The individual information of the donor site of the next exon has 0.5 bits more than that of exon k, so = −0.5 bits.
(C) In this example, a variant in the canonical splice site (e.g., the +5 position) reduces the strength of the canonical splice site from 7.5 to 3.0 bits and simultaneously creates a novel cryptic site with an individual information content of 8.3 bits. An example of this is the variant GenBank: NM_000314.7; c.253+2T>C (PTEN [MIM: 601728]), which alters the canonical splice site and simultaneously changes the sequence of a cryptic splice site located 3 nucleotides downstream, resulting in the inclusion of 4 intronic nucleotides in the variant mRNA.47