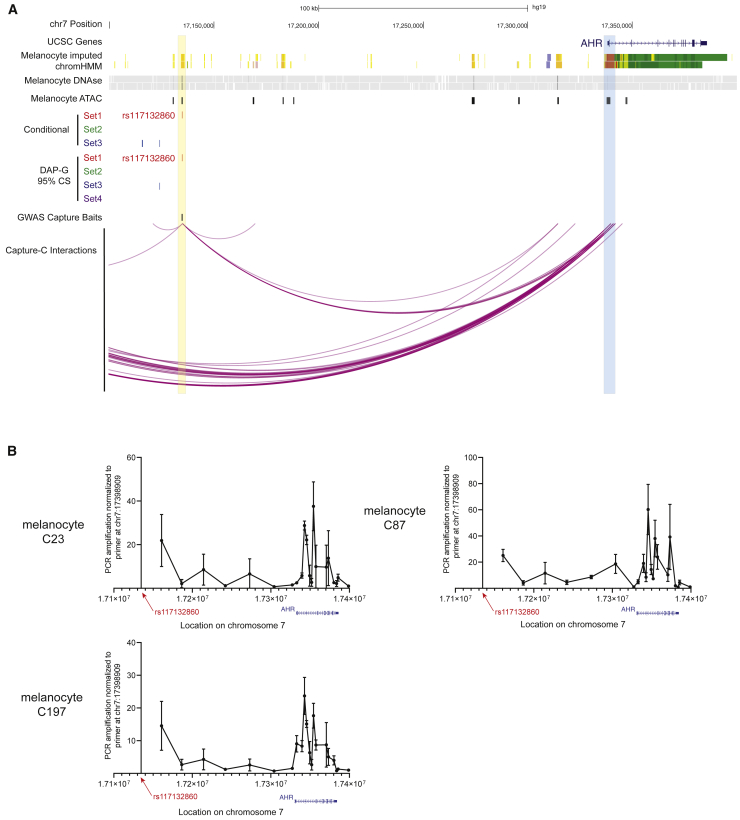
Figure 4.
Region-specific Capture-C and chromatin conformation capture (3C) show a chromatin interaction between rs117132860 and the AHR promoter and gene body
(A) Significant chromatin interactions captured by Capture-C between rs117132860 and AHR. Region capture baits are labeled in black, and significant interactions are shown as purple arcs. UCSC genes, imputed ChromHMM and DNaseI hypersensitivity (DHS) data from two melanocyte cultures generated by the RoadMap Project, ATAC-seq data generated from five human primary melanocyte cultures, and candidate causal variant sets nominated by either conditional analysis or Bayesian fine-mapping (95% credible sets for each of four clusters) with DAP-G are also shown. Loops were called from data from five distinct melanocyte cultures (three biological replicates per culture) analyzed together for detection of the most reproducible interactions.
(B) Interactions between rs117132860 and AHR were confirmed via chromatin conformation capture (3C) in three independent primary melanocyte cultures. Relative interaction frequencies of various genomic fragments to the rs117132860 region are shown according to their location in chromosome 7. For each experiment, the PCR amplification for each target primer from 3C libraries were first normalized to the PCR amplification of the target primer from BAC library DNA and subsequently normalized to the PCR amplification of the target primer HindIII17398909, which is immediately downstream of the AHR gene body. A total of four biological replicates were performed (one each for C23 and C87 and two for C197; mean and SEM are plotted for each primer pair).