Figure 4.
Colocalization of cell-type-specific eQTLs with GWAS for brain-related traits
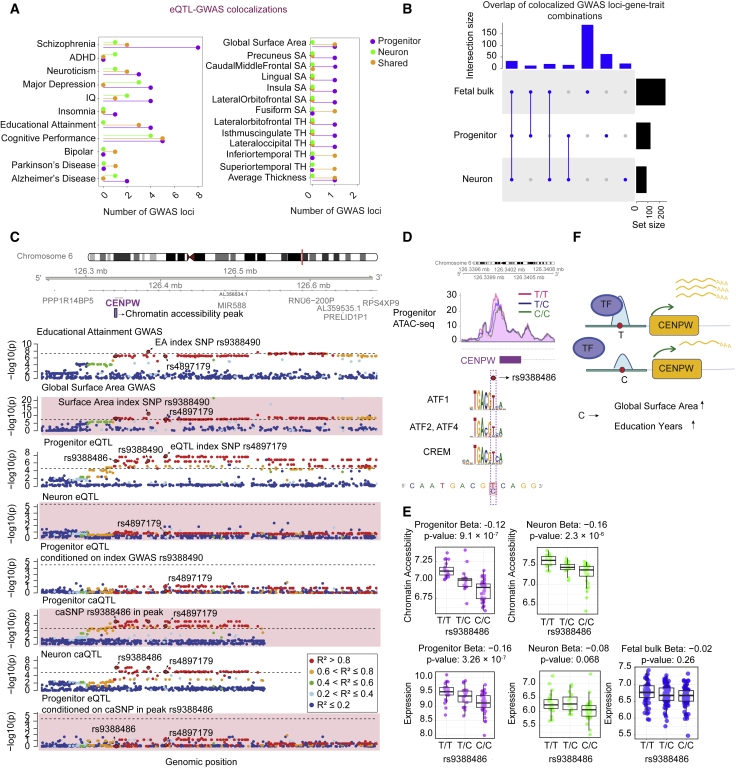
(A) Number of GWAS loci colocalized with progenitor (purple)- or neuron (green)-specific eQTLs or both cell types (orange). Each GWAS trait is listed on the y axis (SA, surface area; TH, thickness).
(B) LD-based overlap of colocalized GWAS loci-gene pairs per trait combinations across progenitor, neuron, and fetal bulk eQTL colocalizations for the traits listed in (A).
(C) Genomic track showing regional association of variants with educational attainment (EA), global surface area (GSA), and CENPW expression in progenitors and neurons, −log10 of association p values on the y axis, and genomic location of each variant on the x axis. Progenitor eSNP rs4897179 (3rd row) was coincident with index SNP (rs9388490) for both EA (1st row) and GSA GWAS (2nd row), and conditioning progenitor eSNP rs4897179 on rs9388490 showed colocalization of the two signals (5th row). Also, rs4897179 was colocalized with another variant (rs9388486) located in the chromatin accessibility peak at the promoter of CENPW (6th and 8th rows). Genomic tracks were color-coded based on LD r2 relative to the variant rs9388486. Dashed line indicates significance threshold.
(D) Plot showing the chromatin accessibility peak (chr6:126,339,531–126,340,960) in progenitors across different genotypes of rs938848. The C allele of rs9388486 disrupted binding motifs of transcription factors including CREM, ATF1, ATF2, and ATF4.
(E) Boxplots showing chromatin accessibility across rs9388486 genotypes in progenitors (purple) and neurons (green) (top). Boxplots showing VST normalized CENPW expression across rs9388486 genotypes in progenitors (purple), neurons (green), and fetal bulk (blue) (bottom).
(F) A schematic showing that one or more of the implicated transcription factors (TF) has decreased preference to bind at the C allele, which results in lower CENPW expression, increase in global surface area, and educational attainment.