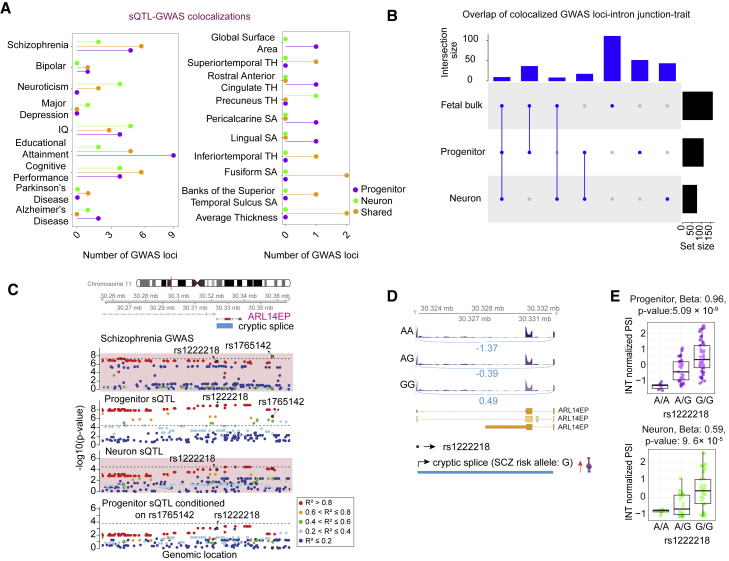
Figure 5.
Colocalization of cell-type-specific sQTLs with GWAS for brain-related traits
(A) Number of GWAS loci colocalized with progenitor (purple)- or neuron (green)-specific sQTLs or both cell types (orange). Each GWAS trait is listed on the y axis (SA, surface area; TH, thickness).
(B) LD-based overlap of colocalized GWAS loci-intron junction pairs per trait across progenitor, neuron, and fetal bulk sQTL colocalizations for the traits listed in (A).
(C) Genomic tracks color-coded based on pairwise LD r2 relative to the variant rs1222218 showing regional association of variants with SCZ and an unannotated alternative splicing event for ARL14EP in progenitors and neurons, association p values on the y axis, and genomic location of each variant on the x axis. A cryptic exon skipping splice site (chr11:30,323,202–30,332,866) was associated with progenitor sSNP (rs1222218) colocalized with SCZ GWAS index SNP (rs1765142). Dashed line indicates significance threshold.
(D) Sashimi plots with the gene model of ARL14EP and the genomic position of the unannotated splice site (blue) overlapping with ARL14EP. Average INT normalized PSI values for the splice site are shown for each genotype group. Schizophrenia risk allele G increases the frequency of the exon skipping event in progenitors.
(E) Boxplots showing INT normalized PSI values for splice across rs1222218 genotypes in progenitors and neurons.