Figure 6.
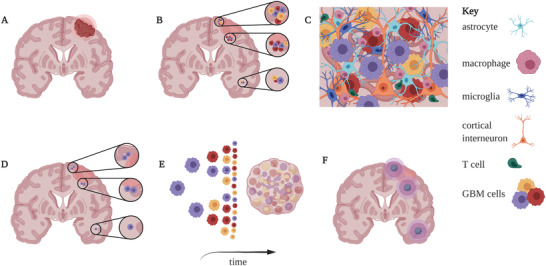
A cartoon representation of the current pathway newly diagnosed GBM patients follow and the most common progression of events (Created with BioRender.com). A) Patient presents to clinic with a brain tumour and receives gross total resection (GTR) surgery. B) Despite GTR and margins, some tumour cells remain close to the resection cavity, and some may have begun spreading further through the parenchyma. C) A representation of the complex heterogeneity of cell types surrounding GBM cells in the brain microenvironment. D) Following GTR, the patient receives TMZ, and radiotherapy which aims to kill remaining sensitive tumour cells; however some resistant cells persist following the cessation of therapies (shown in purple). E) These persisting cells begin the process of re‐populating the tumour and re‐establishing the original heterogeneity. F) Despite standard of care, the tumour recurs either at sites close to or further afield from the original tumour. Recurrences may present on the ipsilateral or contralateral side.
