Figure 2.
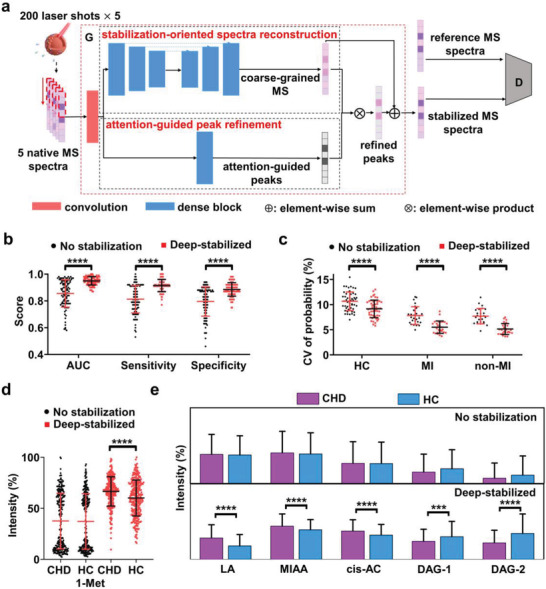
Construction and performance of the deep stabilizer. a) The generative adversarial network structure of the deep stabilizer, which included a generator (G) and discriminator (D). The generator used native MS results as input to produce stabilized MS results through two branches: stabilization‐oriented spectrum reconstruction and attention‐guided peak refinement. A convolutional layer was applied to the two branches (see Experimental Section). The final reconstruction used the attention‐guided peaks and coarse‐grained MS spectra to efficiently reconstruct refined peaks and stabilize the MS results through element‐wise production and addition. The discriminator calculated the probability of the stabilized MS results as the reference MS results. Blue rectangle represented the dense block as the basic feature extraction unit for both branches and the solid arrow referred to the forward feed direction. b) Diagnostic performance (AUC, sensitivity, and specificity) of no stabilization and deep‐stabilized data for the prediction of CHD in the validation cohort. c) CVs of predicted probabilities for HCs and CHD (MI and non‐MI) patients in the validation cohort through no stabilization and deep‐stabilized experiments. d) Data on levels of 1‐methylpyrrole (1‐met) in HCs and CHD patients obtained through no stabilization and deep‐stabilized experiments. e) The newly screened five biomarkers including LA, MIAA, cis‐AC, diacylglycerol (14:1/24:1) (DAG‐1), and diacylglycerol (24:1/20:4) (DAG‐2) through no stabilization and deep‐stabilized experiments. *** indicated p < 0.001 and **** indicated p < 0.0001 in paired‐samples t‐test (b,c) and independent‐samples t‐test (d,e).
