Fig. 3.
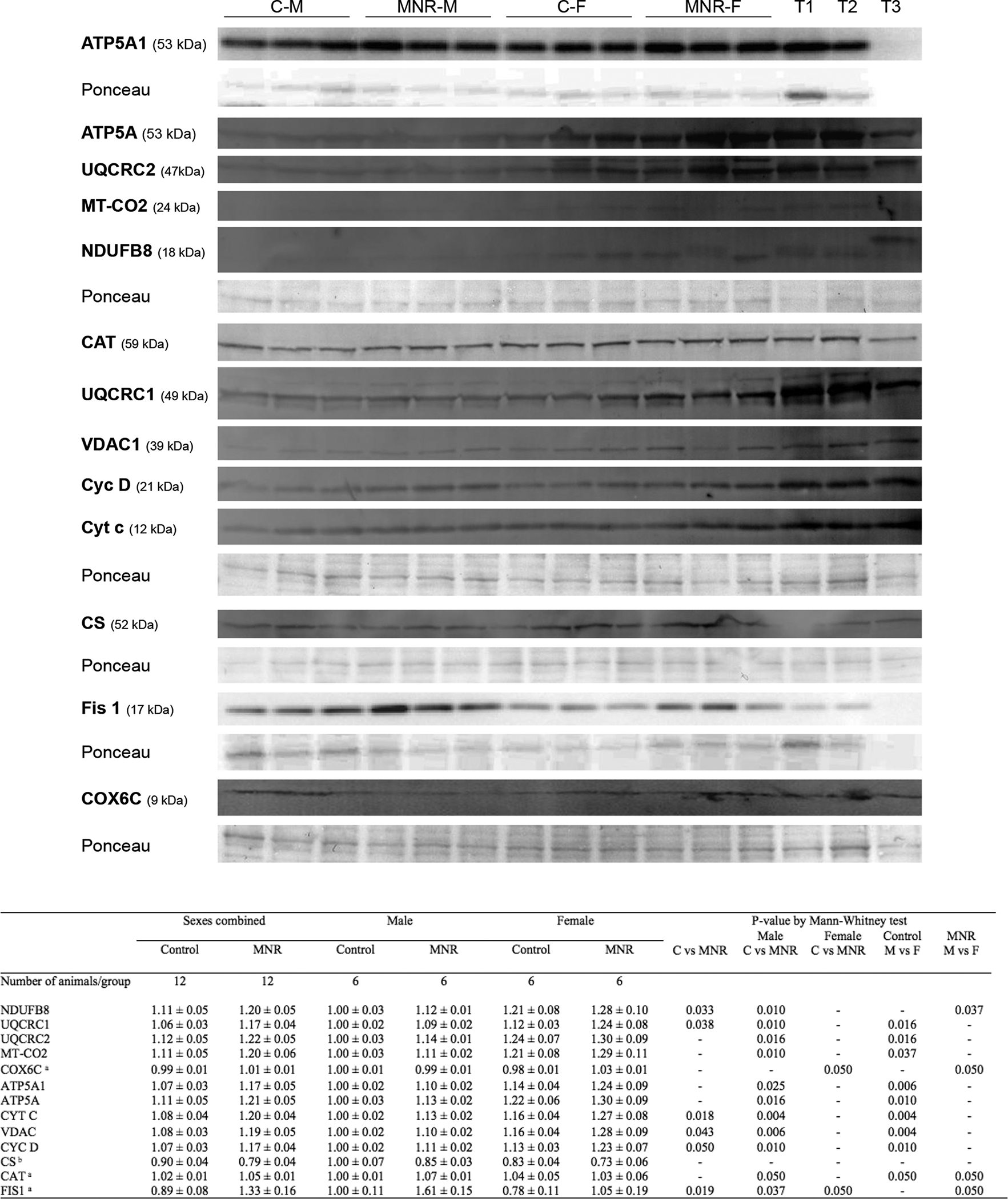
Protein content by immunoblot detection were determined in fetal cardiac LV tissue of control and MNR pregnancies, the latter characterized as 70% of the food consumed by control mothers on a weight-adjusted basis of baboons at 0.9G. C-M, male fetuses from the control group; C-F, female fetuses from the control group; MNR-M, male fetuses from MNR group; MNR-F, female fetuses from MNR group; T1, LV cardiac sample from an adult male baboon; T2, LV cardiac sample from an adult female baboon; T3, human cardiac sample, not used in all membranes. Ponceau staining for the respective membrane was used for normalization and as a loading control. Data are presented as arbitrary units and represent densitometry analysis of membranes by immunoblot detection after image acquisition. Data are means ± SEM; n=6 (when separated by sex) or n=12 (sexes combined) animals/group. Comparison between groups was performed using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney test. P-value less than 0.05 was considered significant. See also Table S1–S2.
a for these proteins, the sample size is different from the one previously indicated, being n=3 (when separated by sex) or n=6 (sexes combined) animals/group
b for the CS protein, the sample size is different from the one previously indicated, being n=4 (when separated by sex) or n=8 (sexes combined) animals/group.
