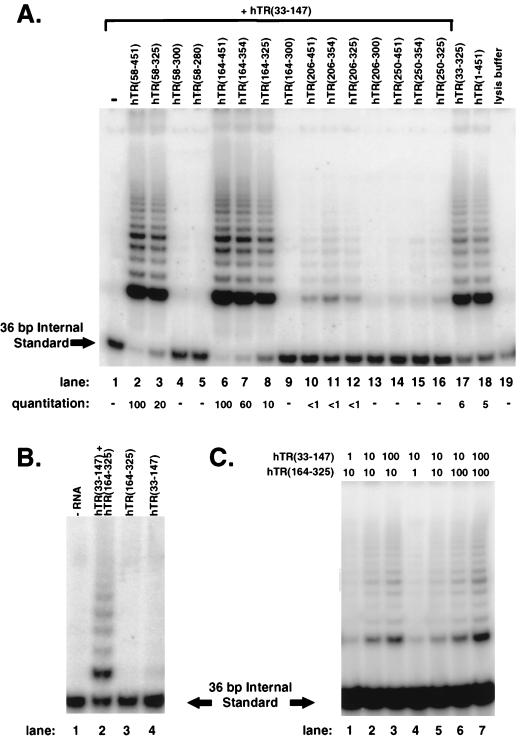
FIG. 7.
Complementation of hTR(33-147) with hTR truncations that lack a template to assemble active telomerase. Assembly reactions were performed with hTERT that was synthesized in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (A and C) or in VA13 cells (B), and 1/20 of each assembly reaction product was examined by the TRAP assay. (A) Assembly reactions for lanes 1 to 16 contained 250 ng of hTR(33-147) (7 pmol, the molar equivalent to 1 μg of full-length hTR) and either no additional RNA (lane 1) or a 1/10 molar equivalent amount (0.7 pmol) of the nontemplating RNAs, as indicated (lanes 2 to 16). The assembly reaction for lane 17 contained 70 ng (0.7 pmol) of gel-isolated hTR(33-325); lane 18 contained 100 ng (0.7 pmol) of hTR(1-451). Yeast tRNA (3.3 μg) was included in each sample. Lane 19 is a lysis buffer control to demonstrate the specific assembly of active telomerase. Relative quantitation is shown for this representative TRAP assay and reflects the ratio between the abundance of extended products versus the 36-bp internal standard. (B) S100 extracts prepared from VA13 cells that express exogenous hTERT did not yield telomerase activity when assayed alone (lane 1) or when mixed with either hTR(164-325) (lane 3) or hTR(33-147) (lane 4). However, combining hTR(33-147) and hTR(164-325) with VA13-hTERT extracts yielded telomerase activity in vitro (lane 2). (C) Titration experiments were performed with hTR(33-147) and hTR(164-325). Relative amounts of the RNAs included in the assembly reactions are shown, with 1 U representing 0.07 pmol, which is the molar equivalent of 10 ng of hTR(1-451). When 7 pmol of hTR(33-147) or hTR(164-325) was tested individually in the assembly reactions, no telomerase products were detected (data not shown).