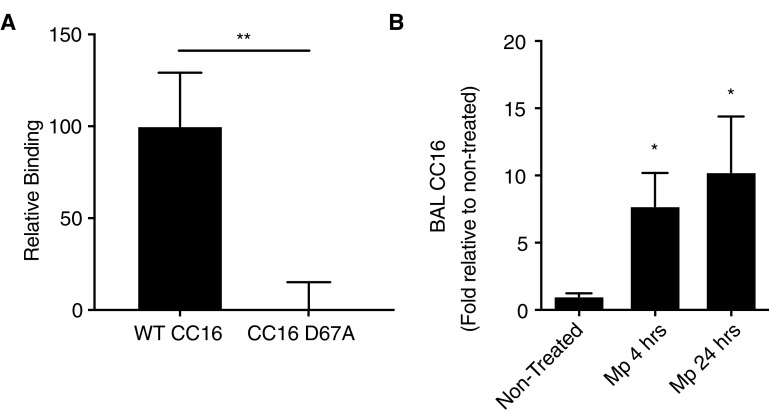
Figure 2.
Binding of recombinant CC16 (club cell secretory protein) (rCC16) to α4β1 integrin complex and relative abundance of CC16 during Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Mp) infection. (A) Plate-binding assays were conducted with human recombinant CC16 with (WT CC16) and without the leucine–valine–aspartic acid sequence (CC16 D67A) that were generated with a histidine tag. The His-tagged rCC16 protein was used to saturate nickel-coated plates and recombinant human integrin subunit α4 was combined with β1 to make the α4β1 integrin complex. Combined integrins were added to the plate-bound rCC16 for 1 hour, after which the plate was washed, and a fluorescent anti-α4 antibody was used to detect the CC16-bound integrin by relative fluorescent intensity. The CC16 to the anti-α4 antibody control was subtracted from each sample to give a final relative binding. Binding assays were conducted (n = 3 replicates) and averaged; **P < 0.01. (B) BAL fluid was examined for CC16 concentrations in nontreated and Mp-infected mice after 4 and 24 hours by Western blot and densitometry analysis. n = 3–5 mice/group; *P < 0.05 compared with nontreated control mice by one-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons. WT = wild-type.