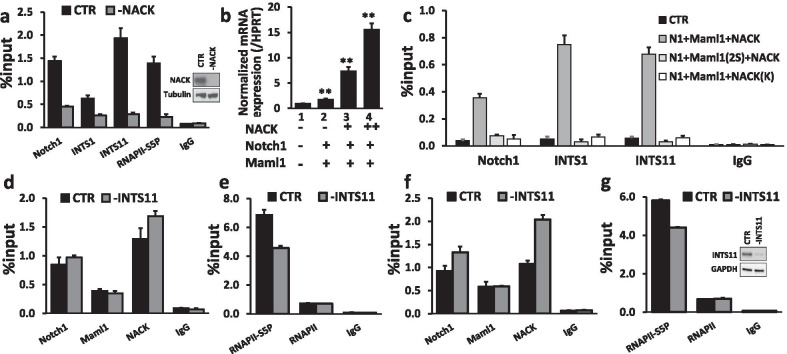
Fig. 2.
Integrator and NACK are required for the activated form of RNAPII phosphorylated at Ser5 (RNAPII-S5P) and other transcriptional co-factors on the Notch-dependent promoter. a Representative ChIP shows that the loss of NACK results in the decrease of Notch1, INTS1, INTS11, and RNAPII-S5P, required for transcriptional elongation, on the HES1 promoter. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). WB shows depletion of NACK b In HEK293T cells, NACK activates HES5 transcription in a NACK concentration-dependent manner. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). **p < 0.01 versus CTR sample. c Representative ChIP shows that in HEK293T cells expressing mutant Maml1 (Maml1(2S)) or mutant NACK (NACK(K)), NACK is unable to bind the NTC, thus HES5 is not activated due to the absence of Notch1 and INT complex (INTS1, INTS11) on the promoter. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). d Representative ChIP shows that the knockdown of INTS11 does not affect the occupancy of Notch1, Maml1, and NACK on the HES1 promoter. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). e Representative ChIP shows that the knockdown of INTS11 results in a decrease of RNAPII-S5P, but not unphosphorylated RNAPII, on the HES1 promoter. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). f Representative ChIP shows that the knockdown of INTS11 does not affect the occupancy of Notch1, Maml1, and NACK on the HES4 promoter. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). g Representative ChIP shows that the knockdown of INTS11 results in a decrease of RNAPII-S5P, but not unphosphorylated RNAPII, on the HES4 promoter. Bars represent standard deviation (N = 3). WB shows depletion of INTS11