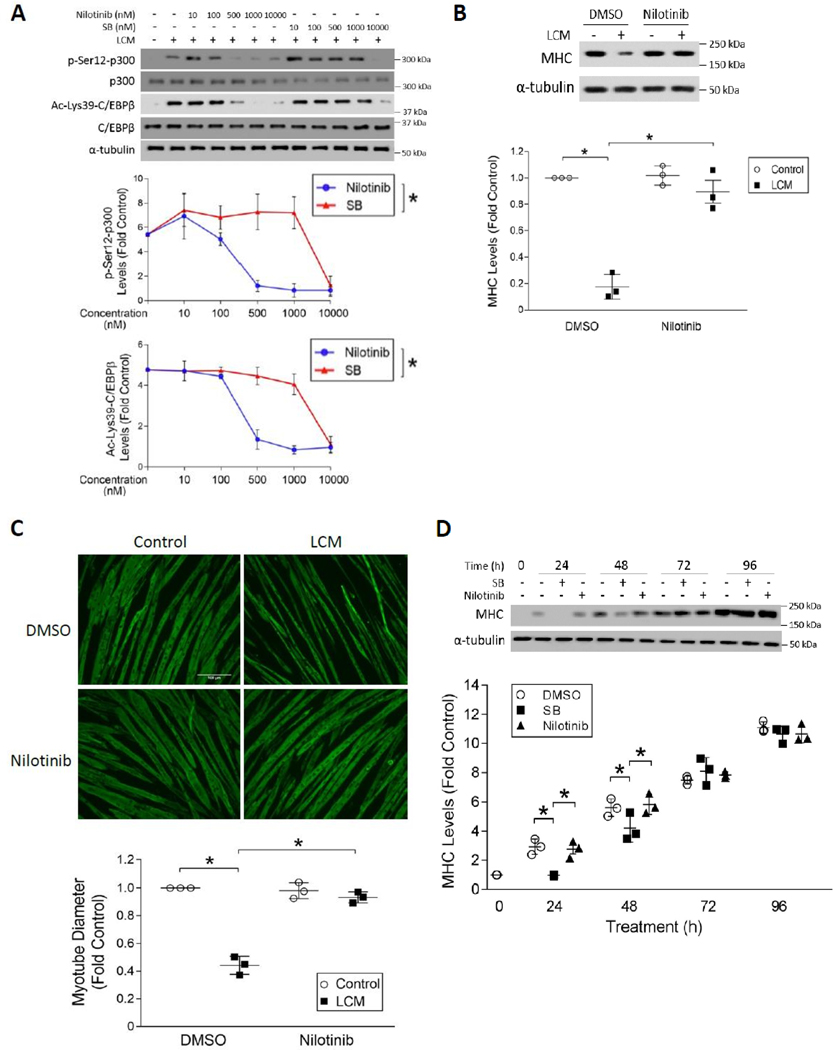
Figure 4. Selective inhibition of p38β MAPK by nilotinib abrogates LLC-induced myotube catabolism without inhibiting myogenesis.
(A) Nilotinib is ~20-fold more potent than SB202190 in the inhibition of LLC-induced activation of p300. C2C12 myotubes were pre-treated with either nilotinib or SB202190 (SB) at indicated doses for 30 mins followed by 2 h of LCM treatment (n = 3). Activation of p300 and C/EBPβ were analyzed by Western blotting as indicated. (B) Nilotinib abrogates LCM-induced loss of MHC in myotubes. Myotubes pre-treated with 500 nM of nilotinib or DMSO were incubated with LCM for 72 hrs. Cell lysates were analyzed for MHC levels by Western blotting (n = 3). (C) Nilotinib abolishes LLC-induced loss of myotube mass. Myotubes treated as described in (B) were subjected to immunofluorescence staining of MHC. Diameter of myotubes was measured. (D) Nilotinib does not suppress myoblast differentiation at the dose that antagonizes LLC-induced myotube atrophy. C2C12 myoblasts were cultured with differentiation medium containing 10 μM SB202190 (SB), 500 nM nilotinib or DMSO for the indicated time periods. MHC content in the cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting at indicated times (n = 3). * signifies a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) determined by one-way ANOVA.