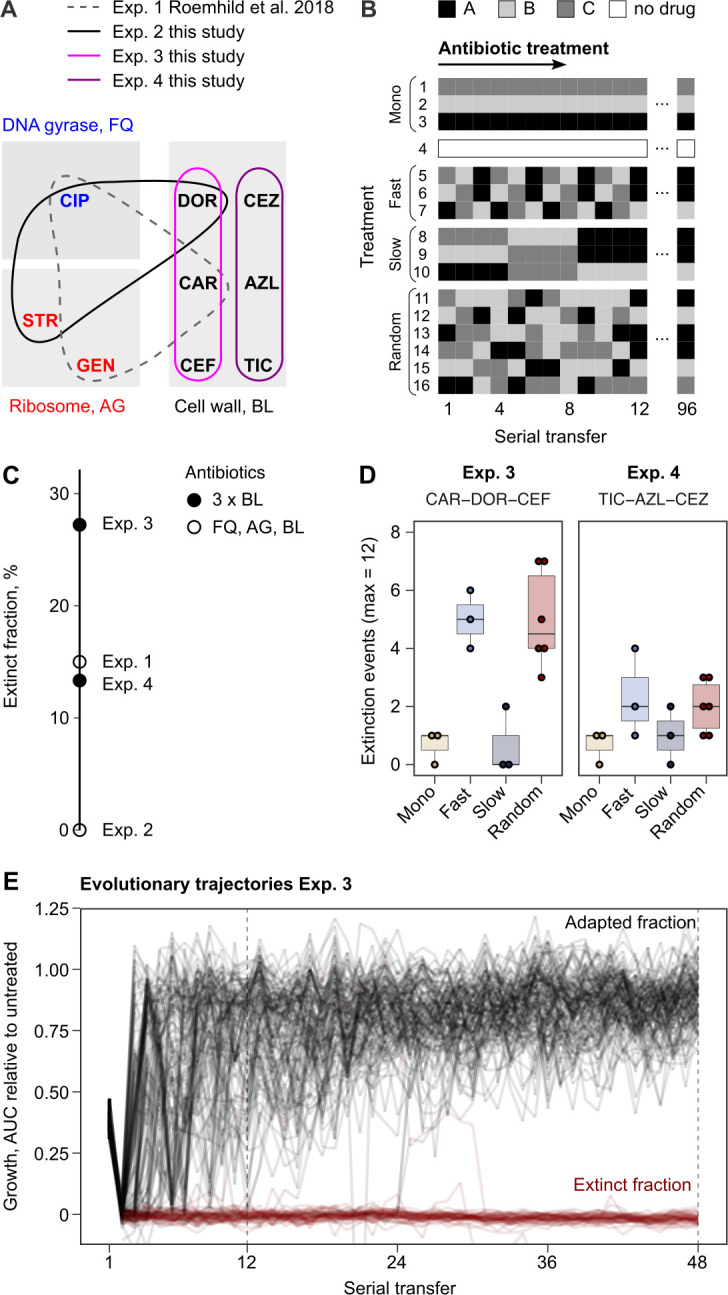
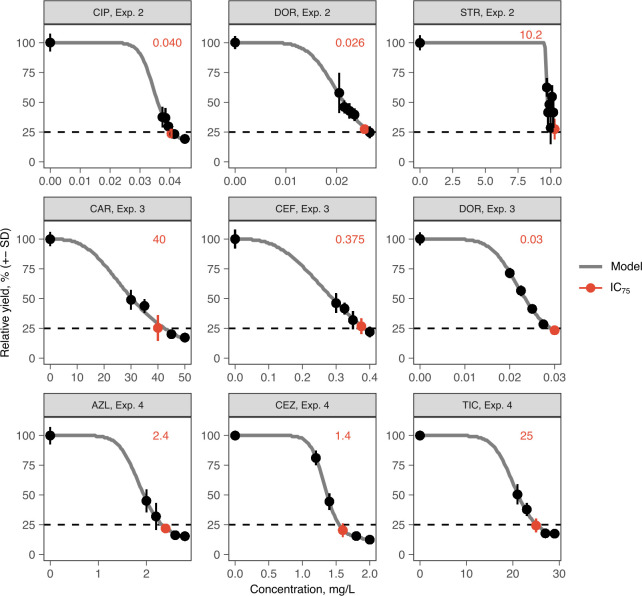
Figure 1. Probability of evolutionary rescue depends on drug triplets and treatment type.
(A) The evaluated antibiotic combinations comprise different types of antibiotic targets. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (FQ) target DNA gyrase, aminoglycosides (AG) inhibit translation, and β-lactams (BL) inhibit cell-wall synthesis. (B) The evaluated treatment protocols test the effects of switching rate and temporal regularity. (C) A fraction of lineages is eradicated by the sublethal dosage sequential treatments. Lineage extinction is high for combinations of cell-wall targeting β-lactams. (D) Variation in extinction for the β-lactam combinations by treatment type (n = 3–6 protocols per treatment type). (E) The distribution of evolutionary trajectories for Exp. 3 with CAR-DOR-CEF shows that the majority of extinction events occur within the first 12 serial transfers (n = 180 lineages). Growth of evolving lineages is quantified relative to untreated reference populations using the relative area under the growth curve (AUC). AZL: azlocillin; CAR: carbenicillin; CEF: cefsulodin; CEZ: ceftazidime; CIP: ciprofloxacin; DOR: doripenem; GEN: gentamicin; STR: streptomycin; TIC: ticarcillin. The following supplementary material is available for Figure 1: Figure 1—figure supplement 1, Figure 1—source data 1, Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1, Supplementary file 1A.