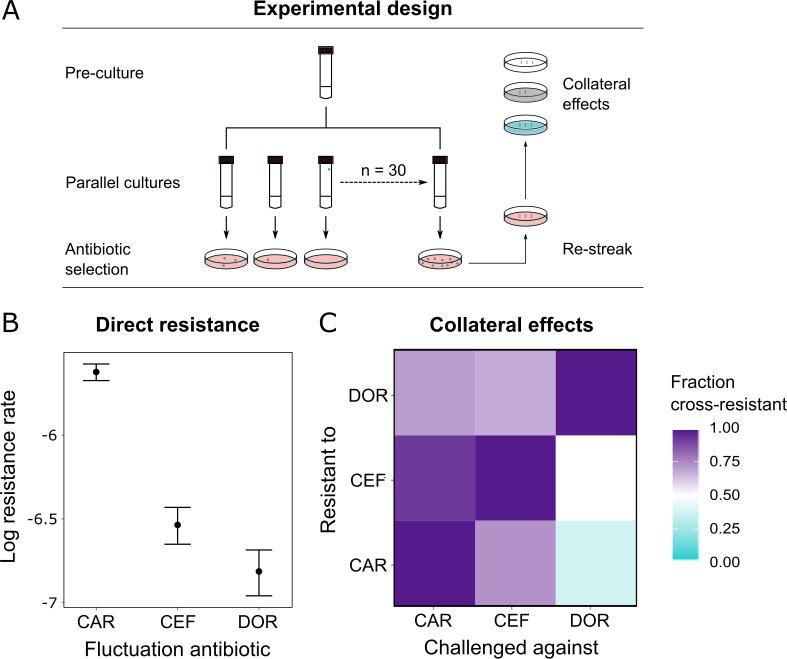
Figure 4. Doripenem has the lowest rates of direct and indirect resistance.
(A) Schematic of the experimental protocol to determine spontaneous rates of resistance on each of the three β-lactams and the resulting collateral landscape. Briefly, an overnight culture was taken and split into 30 parallel cultures where bacteria were allowed to divide in the absence of an antibiotic and any other constraint. Spontaneous resistant mutants were selected on minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) plates and restreaked to ensure genetic resistance. These mutants were then patched on MIC plates of the other two β-lactams to test for cross-resistance. (B) Comparison of rates of spontaneous resistance on the three β-lactams on a Log10 scale. Error bars depict CI95. All comparisons were found to be significantly different from each other (likelihood ratio test; CAR vs. CEF p<0.0001, CAR vs. DOR p<0.0001, and DOR vs. CEF p<0.01). (C) Landscape of collateral effects between the three β-lactams. Fraction of cross-resistant mutants per antibiotic combination is plotted. DOR has the least cases of cross-resistance of the three. A total of 60 mutants per antibiotic were used for collateral effect testing. The following supplementary material is available for Figure 4: Figure 4—source data 1, Supplementary file 1G–I. CAR: carbenicillin; CEF: cefsulodin; DOR: doripenem.