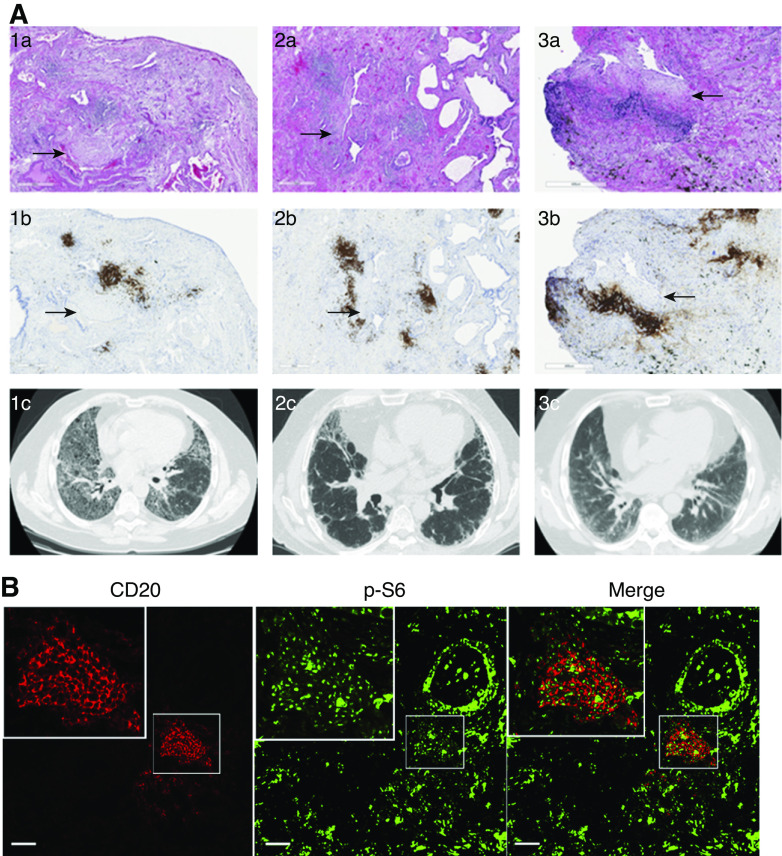
Figure 2.
B-cell aggregates are present in fibrotic areas of the lungs of patients with pulmonary fibrosis and show mTOR activation. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin stain of lung tissue from three patients with clinical diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis (1a–3a) showing pathologic features of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). CD20 stain (1b–3b) demonstrates B-cell aggregates (brown) neighboring fibroblastic foci (arrows). High-resolution computed tomography imaging of lung parenchyma of the respective patients demonstrate different patterns of fibrotic changes (1c–3c). (B) FFPE from patients with pathological findings of UIP underwent immunofluorescent staining for CD20 (red) and p-S6 (green). Scale bars, A, 500 µm; B, 500 µm;. FFPE = formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue.